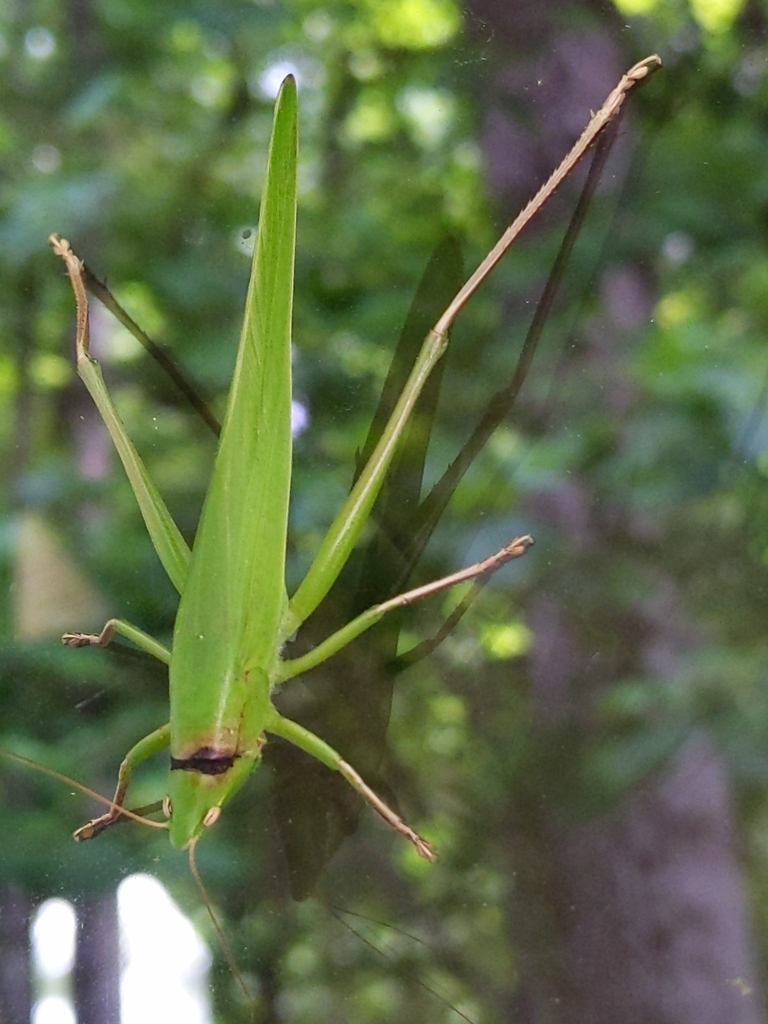




Neoconocephalus triops, the broad-tipped conehead, is a species of Conocephalus fuscus in the family Tettigoniidae. It is found in the Caribbean and North America.
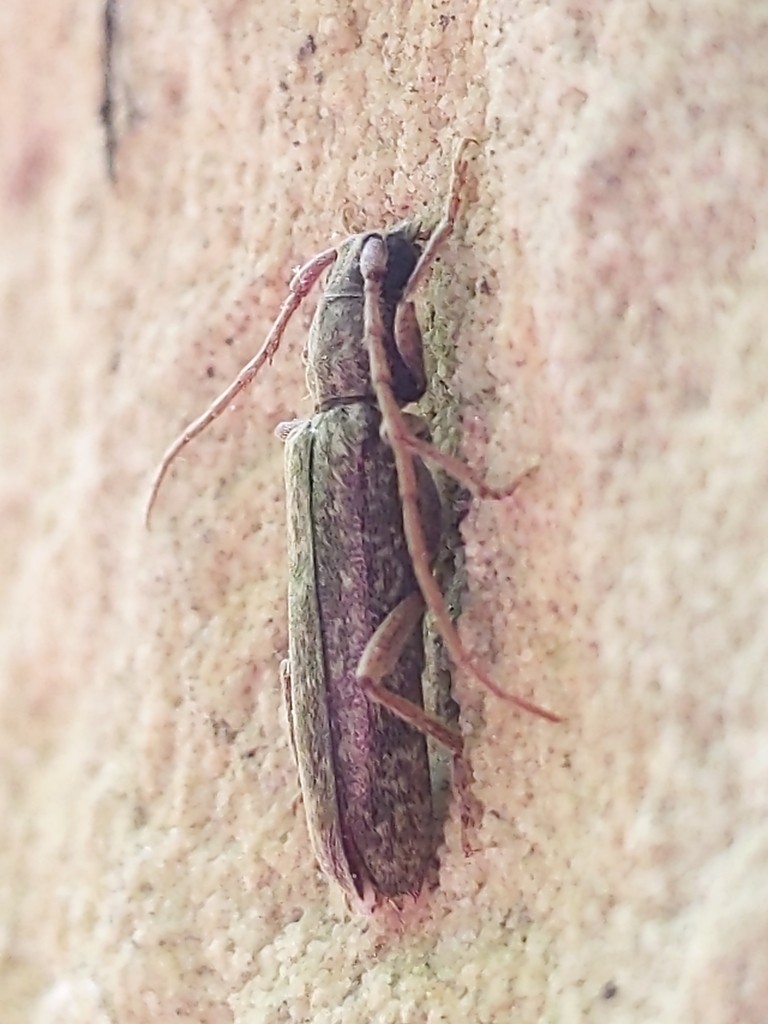
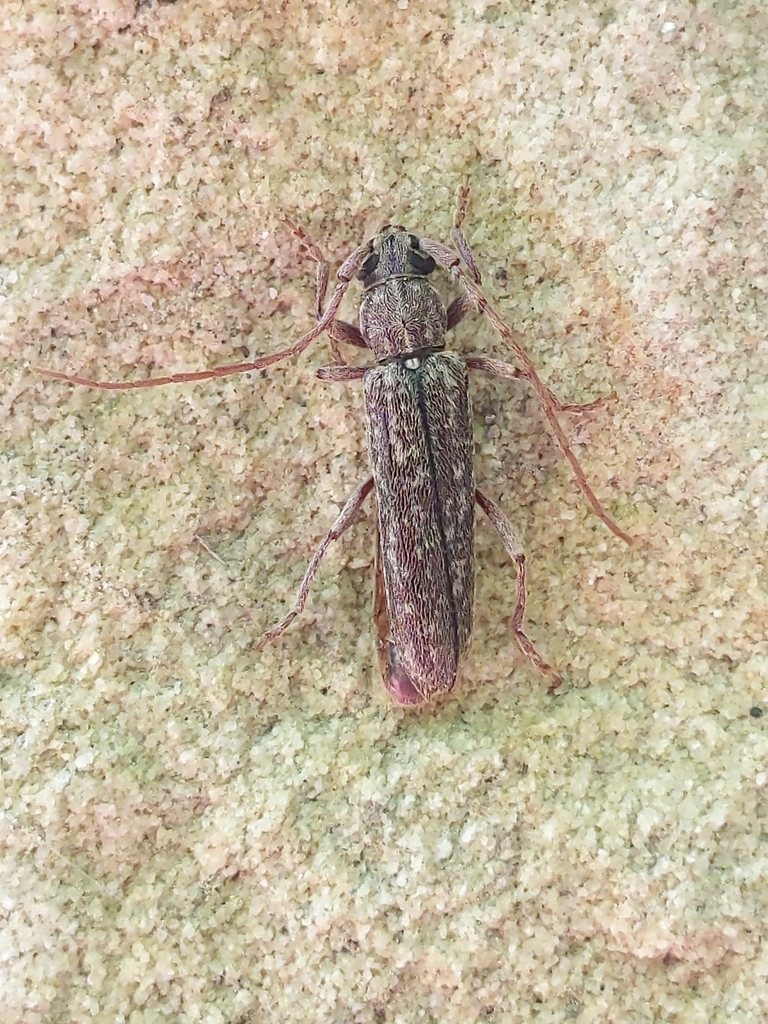


Anelaphus villosus, the twig pruner, is a species in the longhorn beetle family Cerambycidae. It is found in the eastern half of the United States and southeastern Canada.
The species Anelaphus parallelus has been determined to be a taxonomic synonym of Anelaphus villosus. They are now considered the same species under the name Anelaphus villosus.
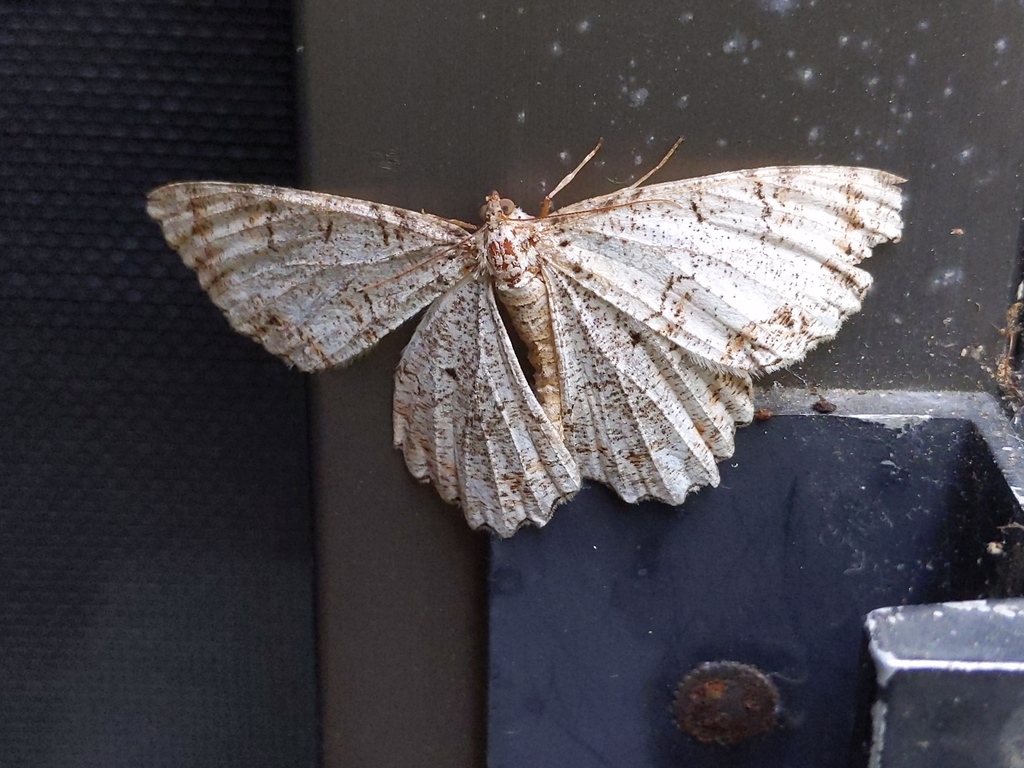


Macaria aemulataria, the common angle moth, is a moth in the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found from Nova Scotia to Florida, west to Texas, north to Oregon and Alberta.
The wingspan is 20\u201322\u00a0mm (0.79\u20130.87\u00a0in). The forewings are cream-grey with three transverse lines and a bold brown patch in the middle outer third. The hindwings have a discal spot and antemedian and postmedian lines. Adults are on wing from mid-June to mid-July in Alberta and from May to September in Ohio.
The larvae feed on Acer species.

Stramonita is a genus of predatory sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Rapaninae of the family Muricidae, the rock snails.

Promachus hinei is a species of robber flies (insects in the family Asilidae).
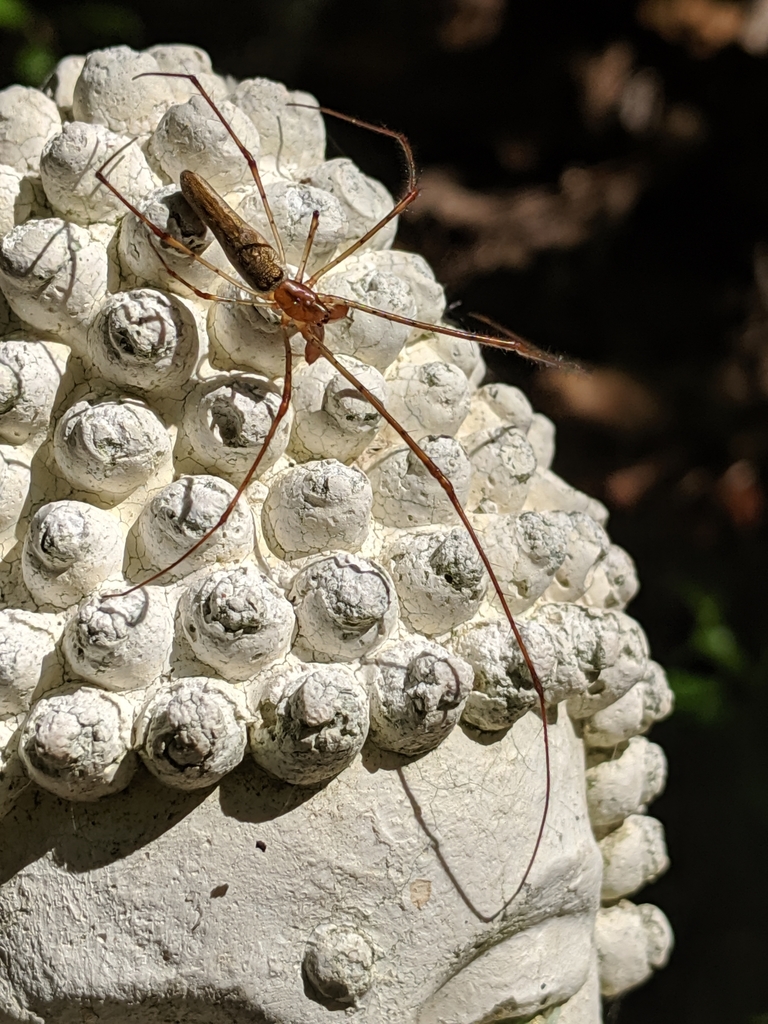


Tetragnatha is a genus of long-jawed orb-weavers found all over the world. It was first described by Pierre Andr\u00e9 Latreille in 1804, and it contains hundreds of species. Most occur in the tropics and subtropics, and many can run over water. They are commonly called stretch spiders in reference to their elongated body form and their ability to hide on blades of grass or similar elongated substrates by stretching their front legs forward and the others behind them. The name Tetragnatha is derived from Greek, tetra- a numerical prefix referring to four and gnatha meaning \jaw\. Evolution to cursorial behavior occurred long ago in a few different species, the most studied being those found on the Hawaiian islands. One of the biggest and most common species is T. extensa, which has a holarctic distribution. It can be found near lakes, river banks or swamps. Large numbers of individuals can often be found in reeds, tall grass, and around minor trees and shrubs.

Tipula furca is a species of large crane fly in the family Tipulidae.
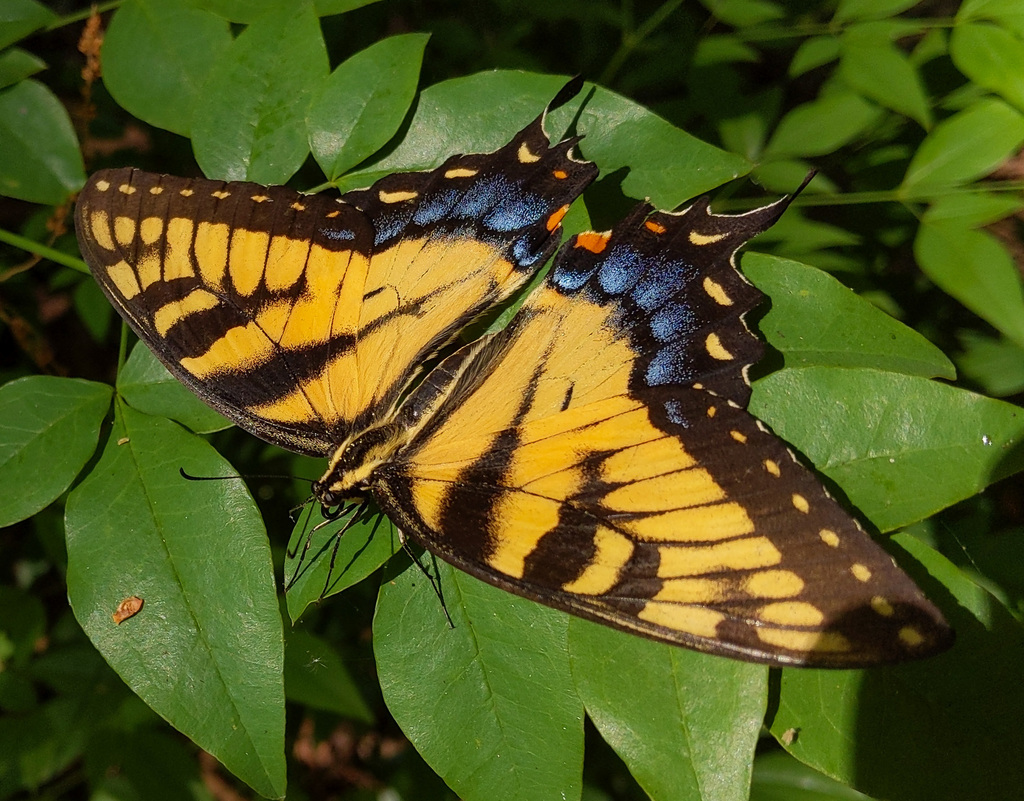


Papilio glaucus, the eastern tiger swallowtail, is a species of butterfly native to eastern North America. It is one of the most familiar butterflies in the eastern United States, ranging north to southern Ontario, Canada, and is common in many different habitats. It flies from spring until fall, during which it produces two to three broods. Adults feed on the nectar of many species of flowers, mostly from those of the families Apocynaceae, Asteraceae, and Fabaceae. P. glaucus has a wingspan measuring 7.9 to 14\u00a0cm (3.1 to 5.5\u00a0in). The male is yellow with four black \tiger stripes\ on each forewing. Females may be either yellow or black, making them dimorphic. The yellow morph is similar to the male, but with a conspicuous band of blue spots along the hindwing, while the dark morph is almost completely black.
The green eggs are laid singly on plants of the families Magnoliaceae and Rosaceae. Young caterpillars are brown and white; older ones are green with two black, yellow, and blue eyespots on the thorax. The caterpillar will turn brown prior to pupating. It will reach a length of 5.5 centimetres (2.2\u00a0in). The chrysalis varies from a whitish color to dark brown. Hibernation occurs in this stage in locations with cold winter months.
The eastern tiger swallowtail is the state butterfly of Alabama (as well as state mascot), Delaware, Georgia, North Carolina and South Carolina, and is the state insect of Virginia.
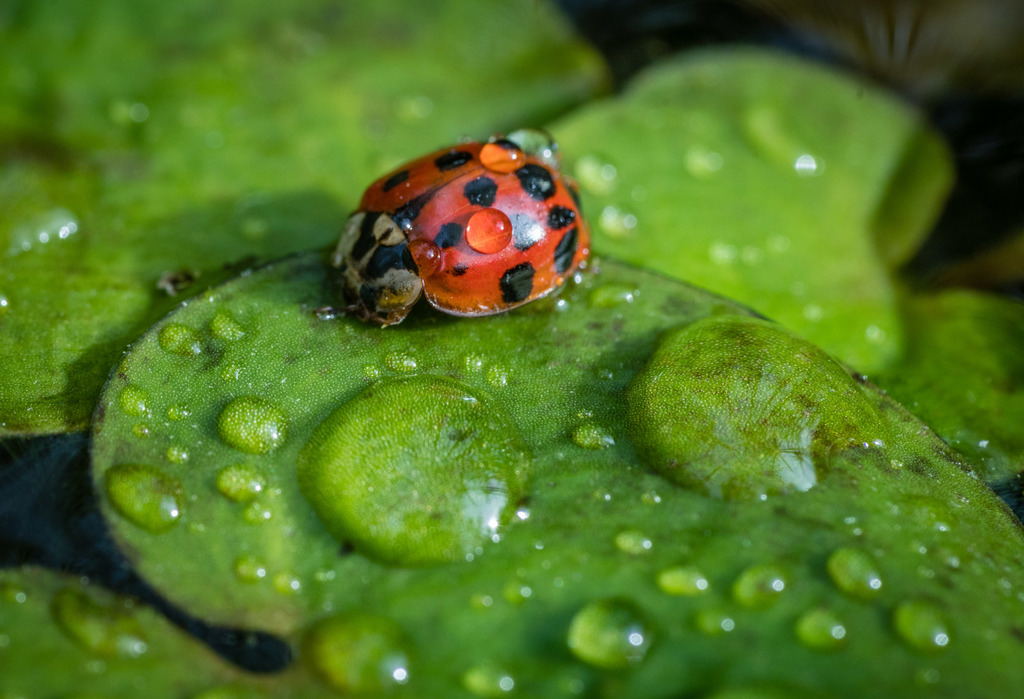

Harmonia axyridis is a large lady beetle or ladybug species that is most commonly known as the harlequin, Asian, or multicoloured Asian lady beetle. This is one of the most variable species in the world, with an exceptionally wide range of colour forms. It is native to eastern Asia, but has been artificially introduced to North America and Europe to control aphids and scale insects. It is now common, well known, and spreading in those regions, and has also established in Africa and widely across South America. This species is conspicuous in North America, where it may locally be known as the Halloween beetle, as it often invades homes during October to overwinter.
When the species first arrived in the UK, it was labelled in jest as the \many-named ladybird\ due to the great quantity of vernacular names. Among those already listed other names include multivariate, southern, Japanese, and pumpkin ladybird.
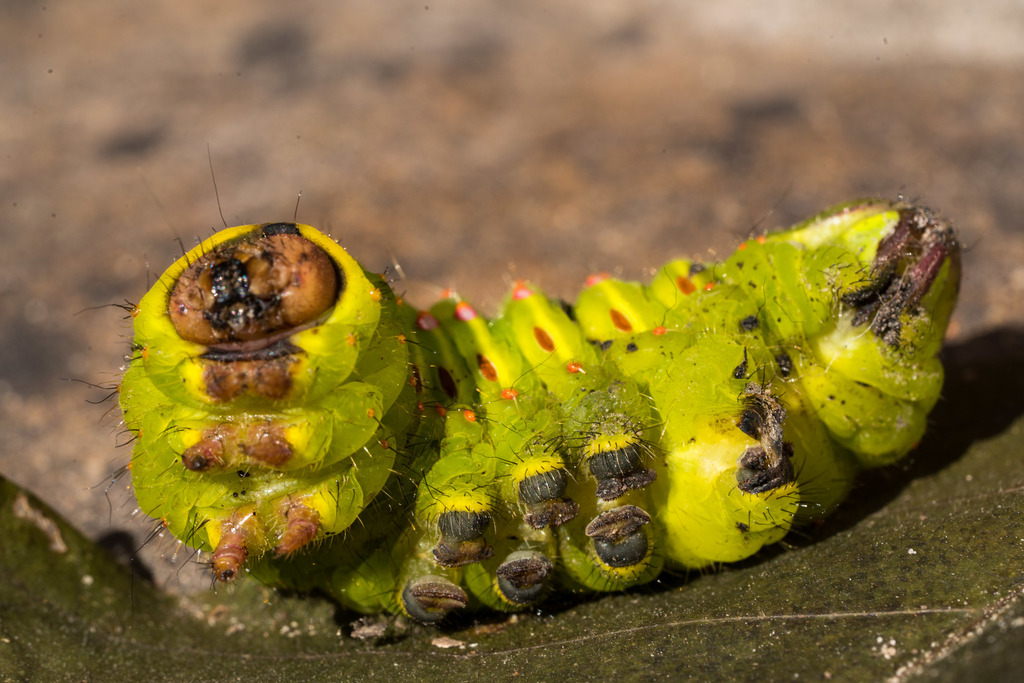
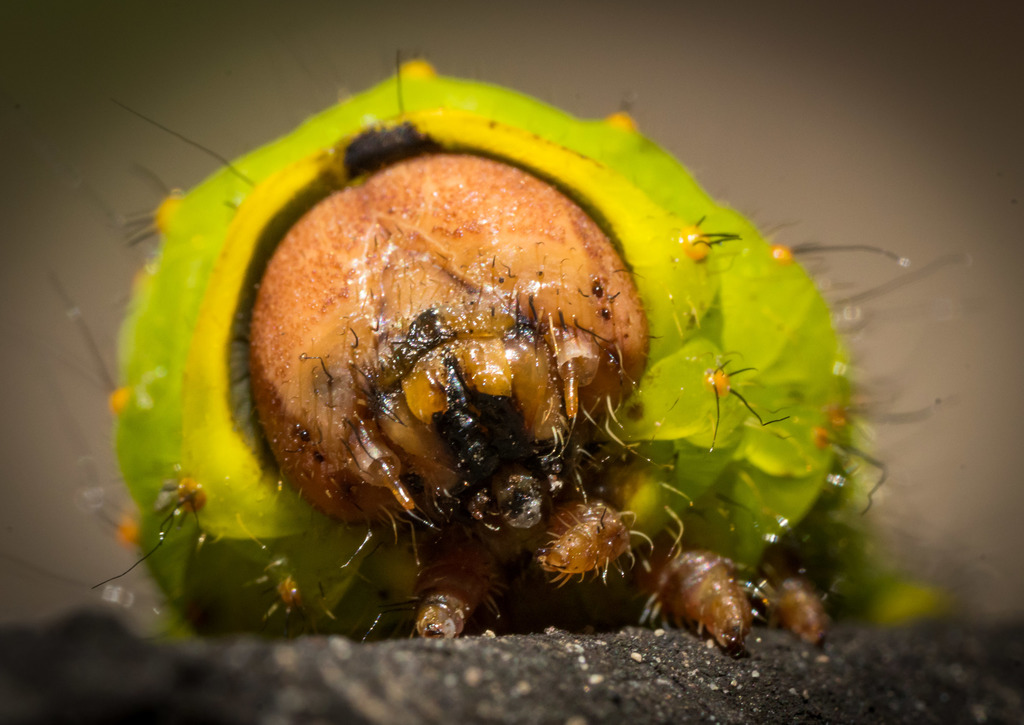



Antheraea polyphemus, the Polyphemus moth, is a North American member of the family Saturniidae, the giant silk moths. It is a tan-colored moth, with an average wingspan of 15\u00a0cm (6\u00a0in). The most notable feature of the moth is its large, purplish eyespots on its two hindwings. The eyespots give it its name \u2013 from the Greek myth of the cyclops Polyphemus. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1776. The species is widespread in continental North America, with local populations found throughout subarctic Canada and the United States. The caterpillar can eat 86,000 times its weight at emergence in a little less than two months. Polyphemus moths are considered to be very polyphagous, meaning they eat from a wide variety of plants

Sarcophaga is a genus of true flies and the type genus of the flesh-fly family (Sarcophagidae). The members of this cosmopolitan genus are frequently known as common flesh flies.
This genus occurs essentially worldwide. These flies are generally well-sized and of a greyish color; like many of their relatives, the typical patterns are lengthwise darker stripes on the thorax and dark and light square dots on the abdomen. Many have conspicuous red compound eyes. These are set further apart in females than in males; the females are also larger on average. As typical for this family, it is almost impossible to tell the species apart from their outward appearance, and many can only be reliably identified by microscopic examination of the males' genitalia.
As the common name implies, their larvae typically feed on decaying meat. Some, however, instead eat the bacteria and other small organisms living on carrion. Many species have adapted to humans, and while they are usually nuisance pests, some are medically significant vectors of pathogens and bacteria. Sometimes, the larvae cause myiasis. Others are parasitoids of pest caterpillars and beneficial in forestry and orchards.
Well-known species are Sarcophaga africa, Sarcophaga bercaea, the grey flesh-fly Sarcophaga bullata, Sarcophaga carnaria, Sarcophaga crassipalpis, the friendly fly Sarcophaga aldrichi and the red-tailed flesh-fly Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis.
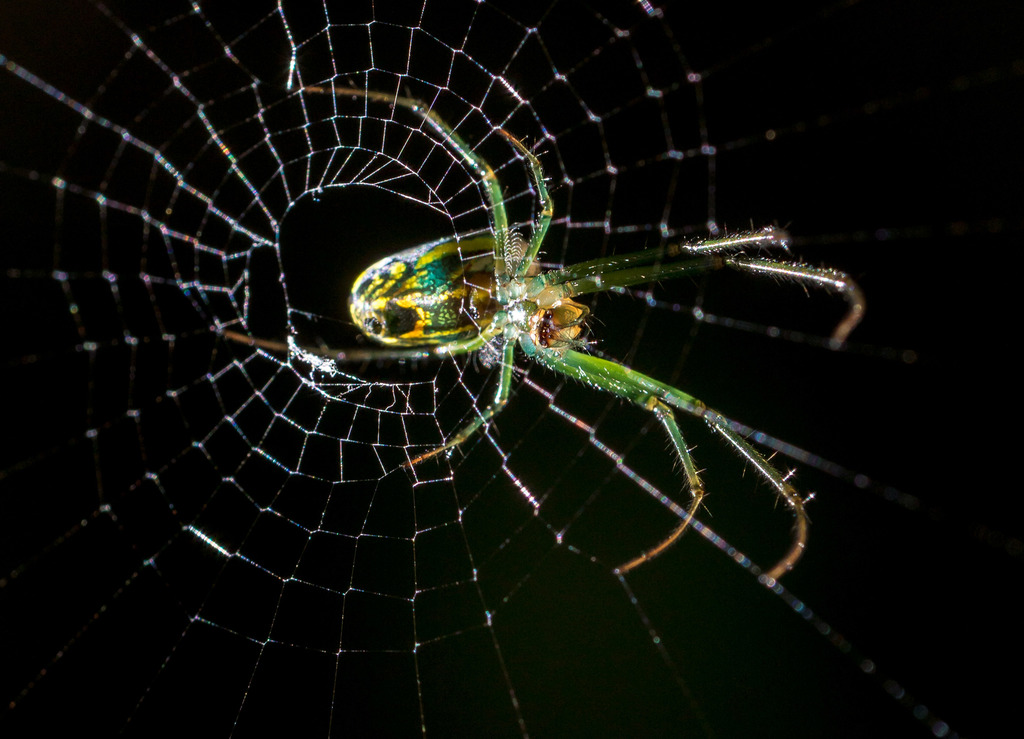
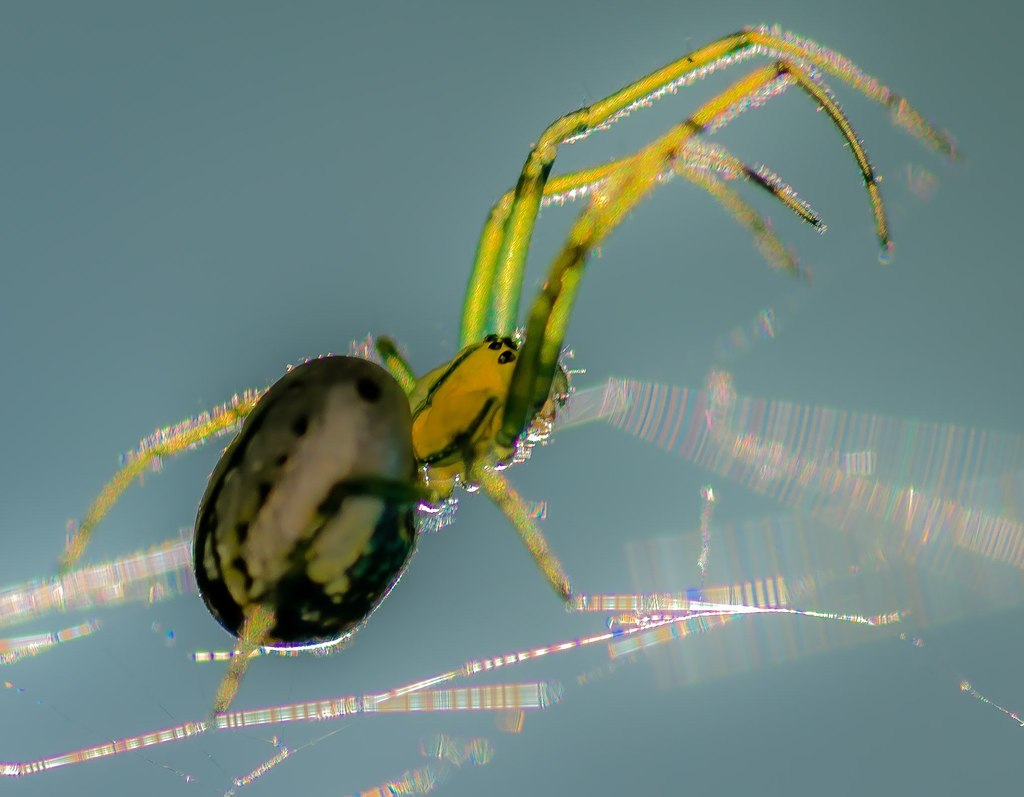
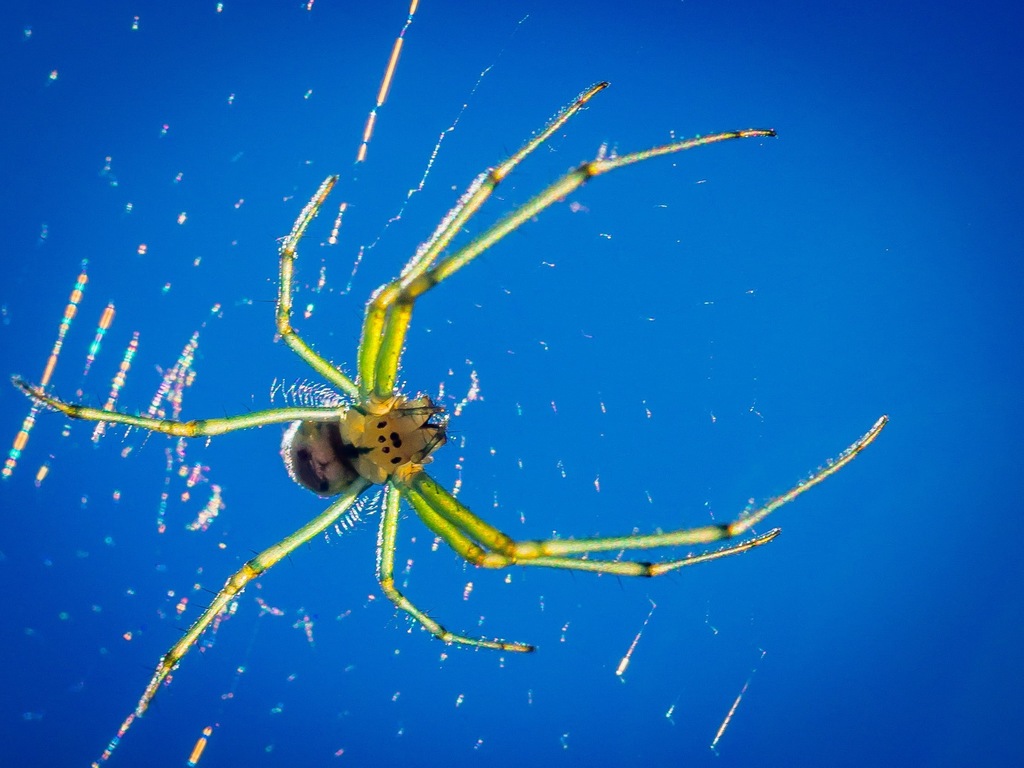



Leucauge venusta, known as the orchard orbweaver spider, is a long-jawed orbweaver spider that occurs from southern Canada to Colombia, along the East coast, reaching into the central US, also in South Asia. The web is often oriented horizontally, with the spider hanging down in the center.
It is distinctively colored, with leaf-green legs and sides (which can sometimes vary to a dark green or even orange). The underside of its thorax is spotted with yellow and black, the top is silvery with brown and black streaks. The neon yellow, orange or red spots on the rear of the abdomen are variable in size among individuals and sometimes absent.
This species is parasitised by a wasp larva which attaches itself externally at the junction of the cephalothorax and abdomen.
A similar species in the same genus is Leucauge mariana.
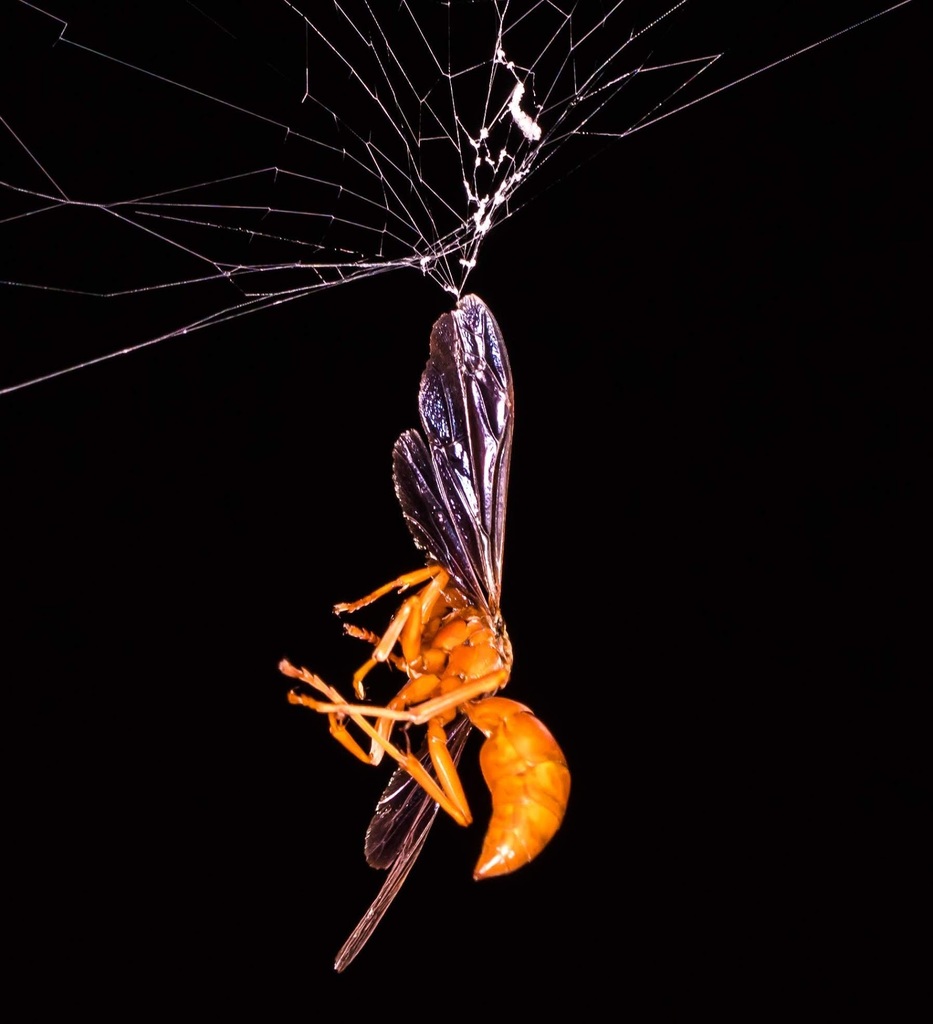

Polistes carolina is one of two species of red paper wasp found in the eastern United States (the other being Polistes rubiginosus) and is noted for the finer ridges on its propodeum. It is a social wasp (subfamily Polistinae) in the family Vespidae. They are native to the United States from Texas to Florida, north to New York, and west to Nebraska. The wasp's common name is due to the reddish-brown color of its head and body. P. carolina prefer to build their nests in protected spaces.
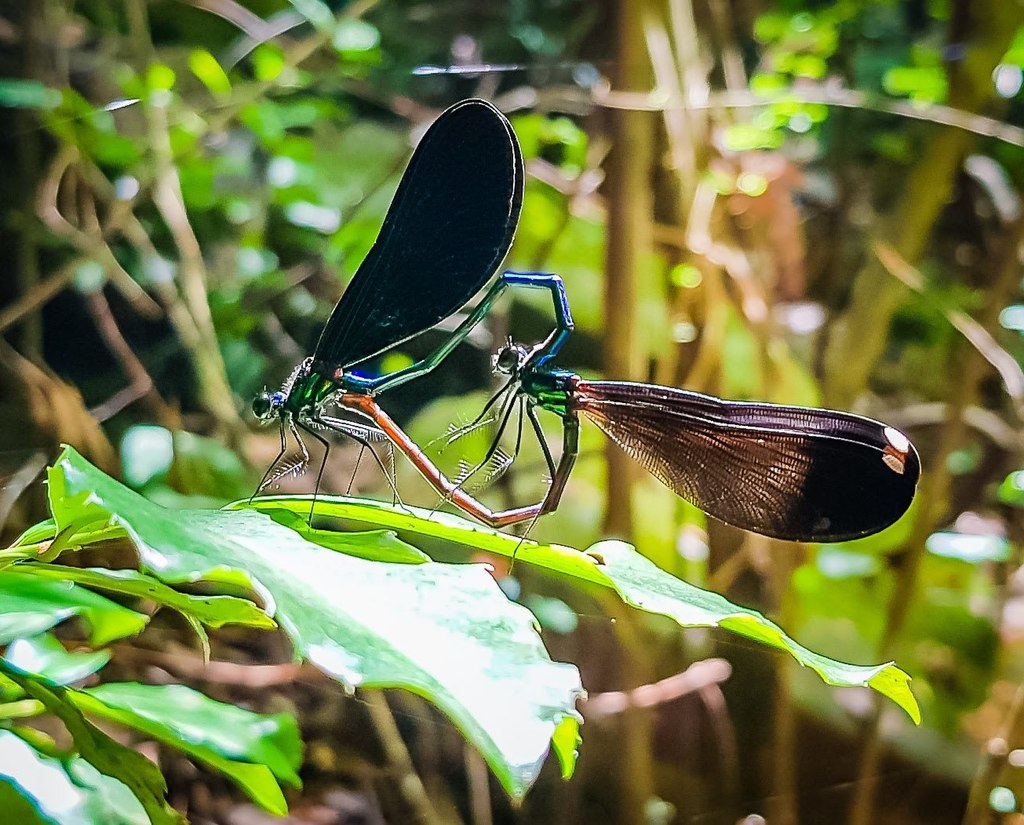


The ebony jewelwing (Calopteryx maculata) is a species of broad-winged damselfly. One of about 150 species of Calopterygidae, it is found in the eastern U.S. and southeastern Canada, ranging west to the Great Plains. Other common names include black-winged damselfly.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (Francisella tularensis). It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms.
Though D. variabilis may be exposed to Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, these ticks are not competent vectors for the transmission of this disease. The primary vectors for B. burgdorferi are the deer ticks Ixodes scapularis in eastern parts of the United States, Ixodes pacificus in California and Oregon, and Ixodes ricinus in Europe. D. variabilis may also carry Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the causative agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the causative agent of human monocytic ehrlichiosis.
Dermacentor ticks may also induce tick paralysis by elaboration of a neurotoxin that induces rapidly progressive flaccid quadriparesis similar to Guillain\u2013Barr\u00e9 syndrome. The neurotoxin prevents presynaptic release of acetylcholine from neuromuscular junctions.
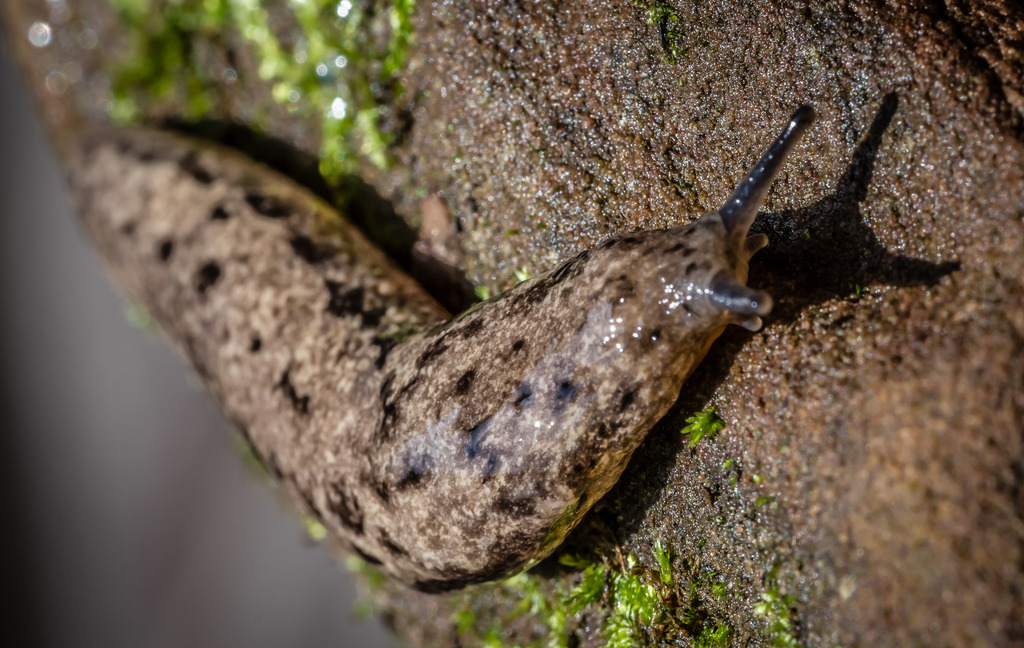


Philomycus carolinianus, also known as the Carolina mantleslug, is a species of land slug. It is a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family of Philomycidae. This species is a part of the fauna of the Carolinian Forest in Canada. This species is also a plays a vital role in the ecosystem through nutrient cycling.
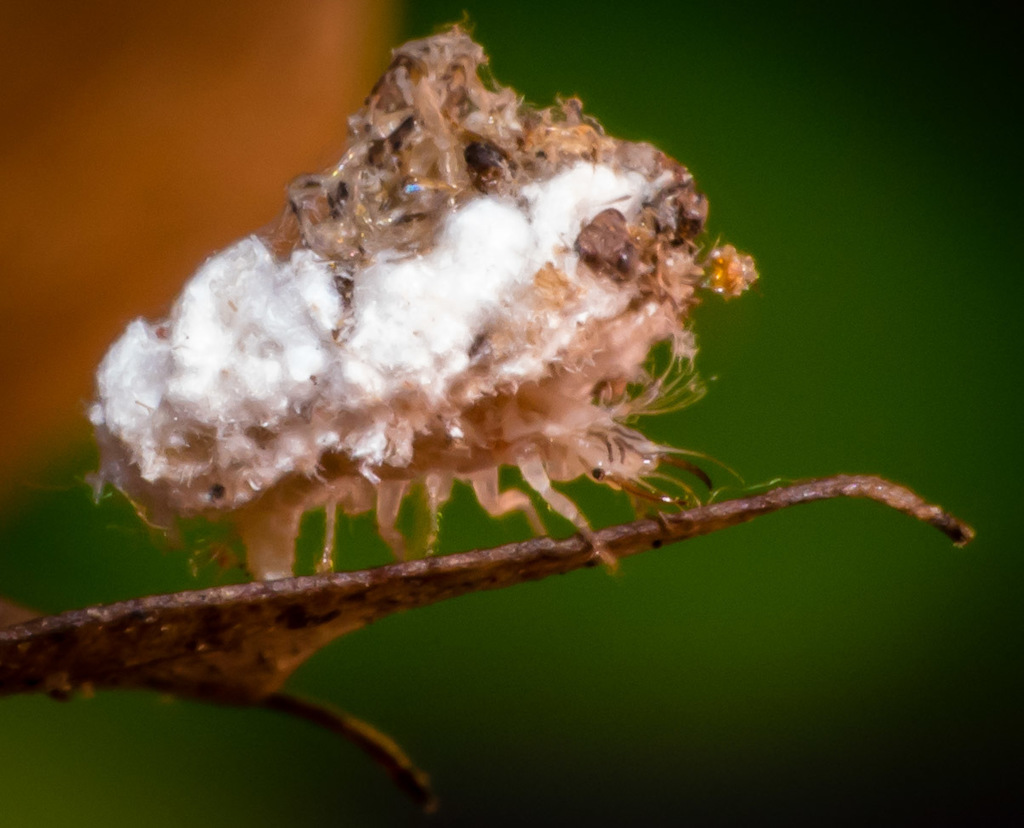
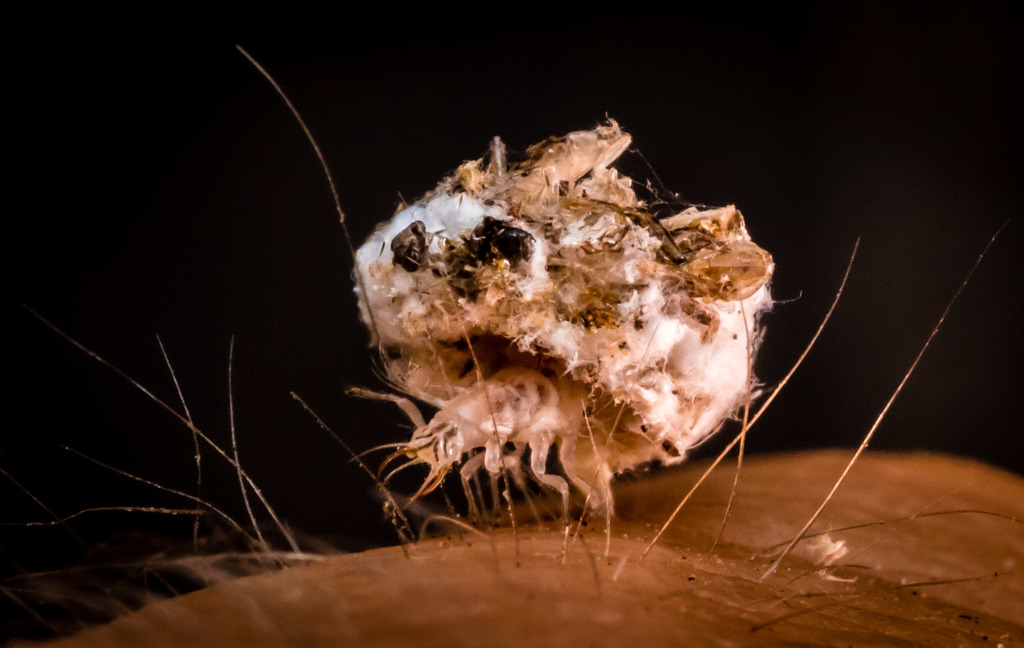

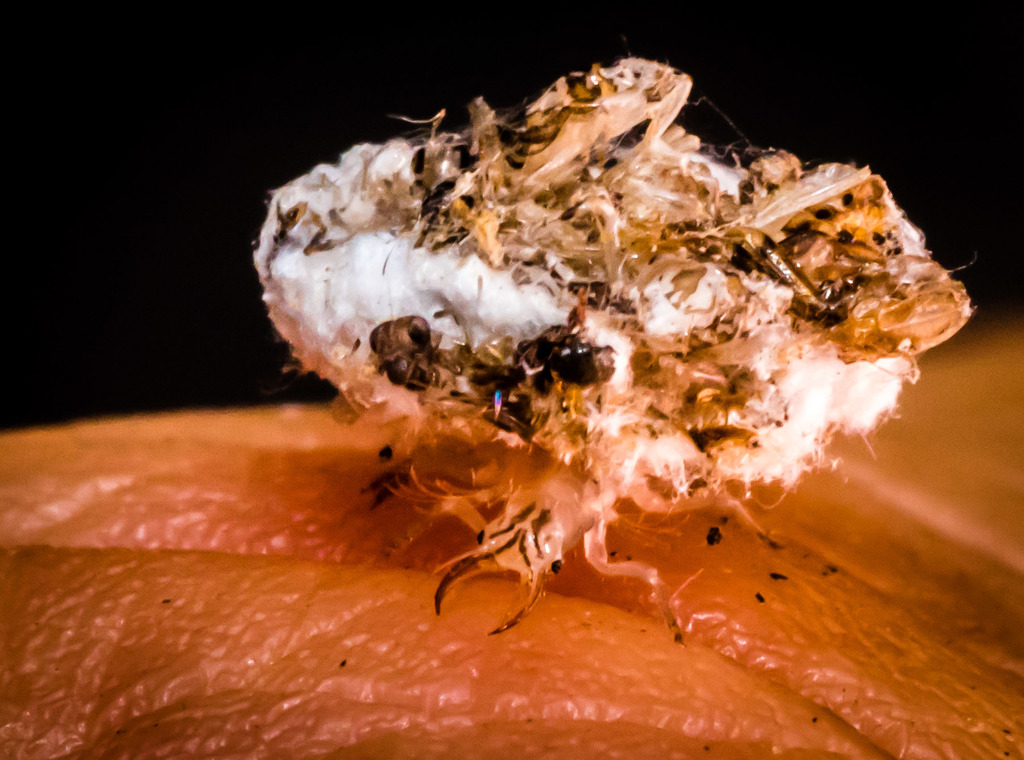

Green lacewings are insects in the large family Chrysopidae of the order Neuroptera. There are about 85 genera and (differing between sources) 1,300\u20132,000 species in this widespread group. Members of the genera Chrysopa and Chrysoperla are very common in North America and Europe; they are very similar and many of their species have been moved from one genus to the other time and again, and in the nonscientific literature assignment to Chrysopa and Chrysoperla can rarely be relied upon. Since they are the most familiar neuropterans to many people, they are often simply called \lacewings\. Since most of the diversity of Neuroptera are properly referred to as some sort of \lacewing\, common lacewings is preferable.
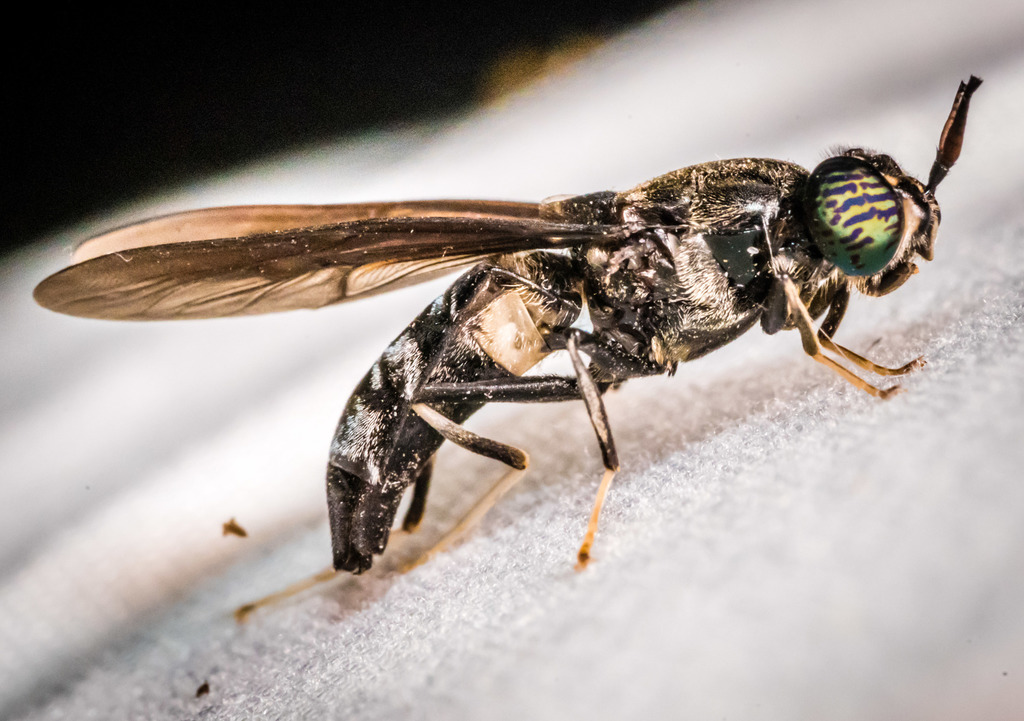

Hermetia illucens, the black soldier fly, is a common and widespread fly of the family Stratiomyidae. Since the late 20th century, H. illucens has increasingly been gaining attention because of its usefulness for recycling organic waste and generating animal feed.
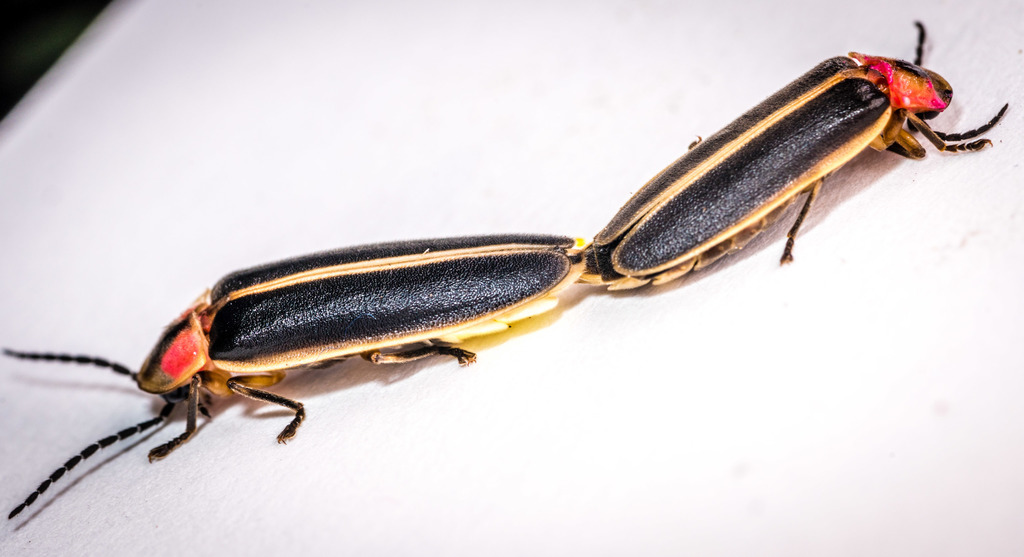


Photinus pyralis, known by the common names common eastern firefly and big dipper firefly, is the most common species of firefly in North America. P. pyralis is a flying and light-producing beetle with a light organ on the ventral side of its abdomen. This organism is sometimes incorrectly classified as Photuris pyralis, which likely results from mistaking the similar-sounding genus Photuris.
The Photuris female may also lure a Photinus pyralis to be eaten to obtain spider-repellent steroids called \lucibufagins\. In males the light organ covers the entire ventral surface of the three most posterior segments and in females it only covers a portion of the third posterior segment. These fireflies are most noticeable around twilight, in the early part of the evening and hover close to the ground. The species' common name refers to the characteristic flight of the male, which flies in a J-shaped trajectory, lighting on the upswing. During flight, the J-shaped flight pattern is used in combination with patrolling flash patterns while seeking a mate. Their flashes are stimulated by light conditions, not by rhythmic impulses as originally thought.
The genome of Photinus pyralis was sequenced in 2018.
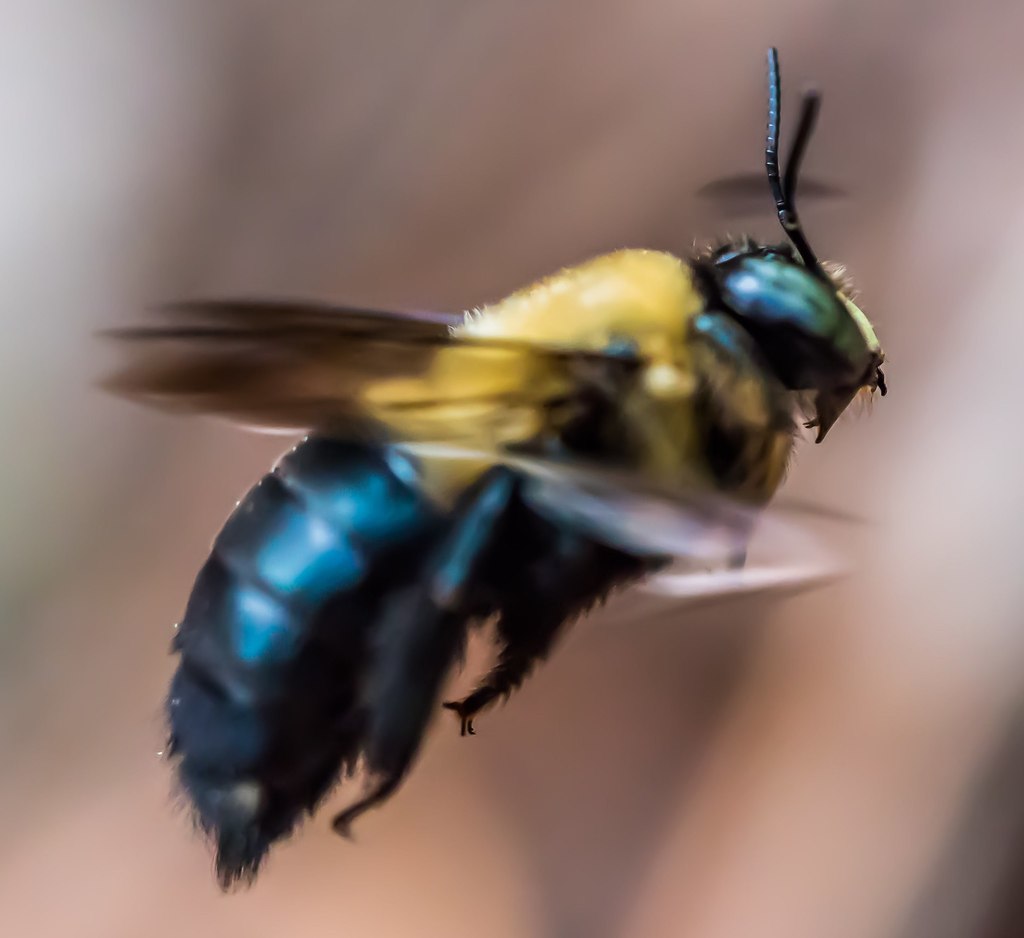



Xylocopa virginica, sometimes referred to as the eastern carpenter bee, extends through the eastern United States and into Canada. They are sympatric with Xylocopa micans in much of southeastern United States. They nest in various types of wood and eat pollen and nectar. In X. virginica, dominant females do not focus solely on egg-laying, as in other bee species considered to have \queens\. Instead, dominant X. virginica females are responsible for a full gamut of activities including reproduction, foraging, and nest construction, whereas subordinate bees may engage in little activity outside of guarding the nest.
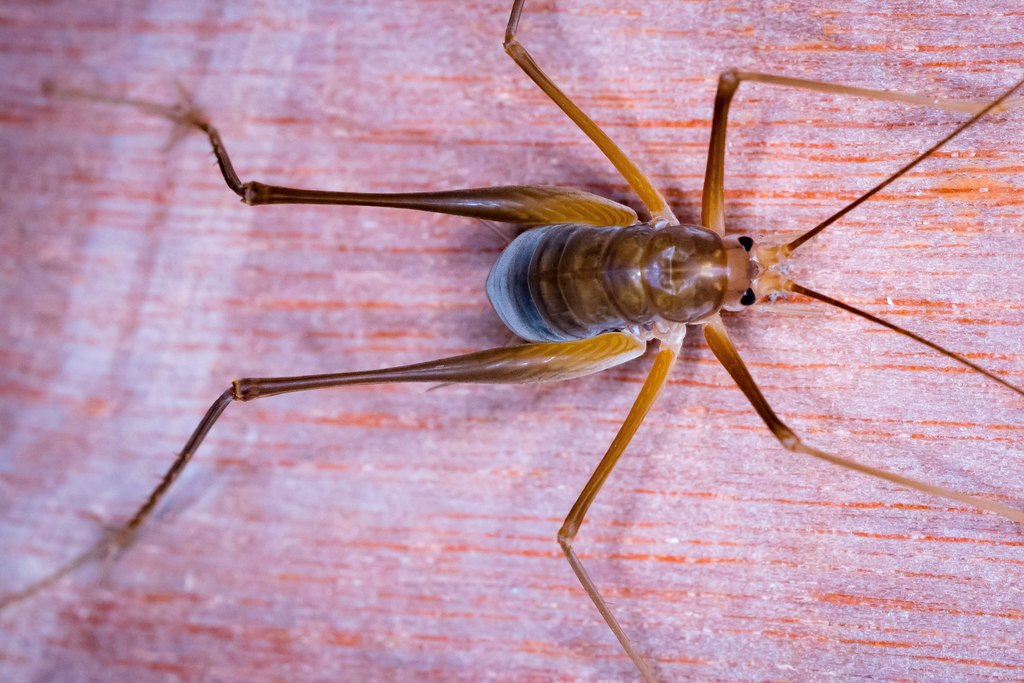
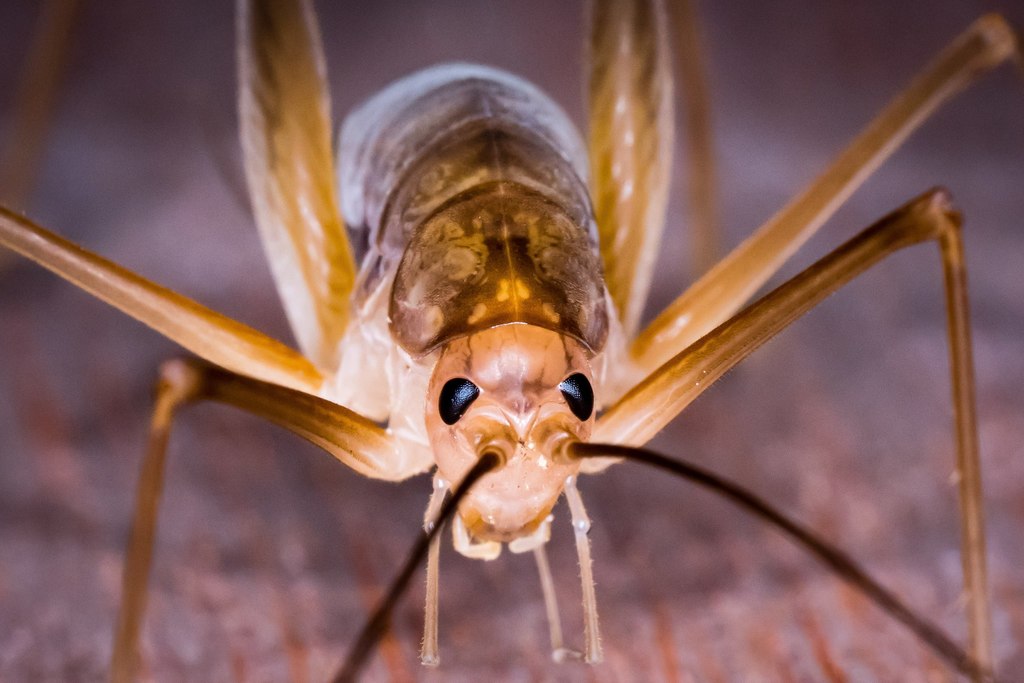



Euhadenoecus is a genus of camel crickets in the family Rhaphidophoridae. There are at least four described species in Euhadenoecus.
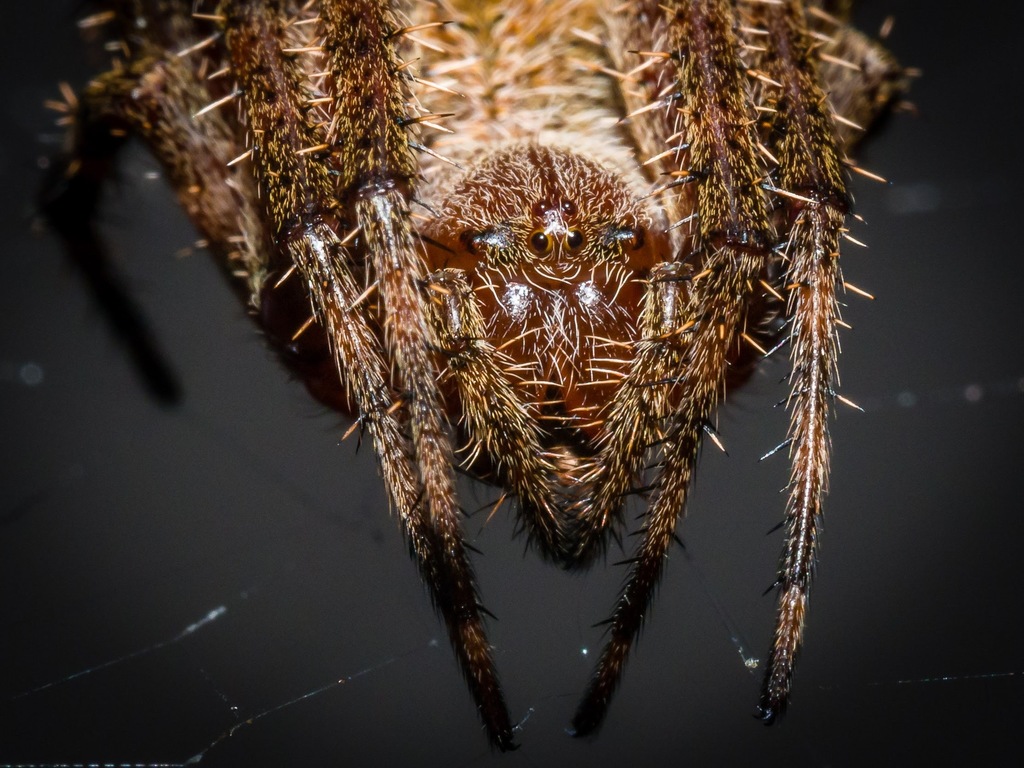
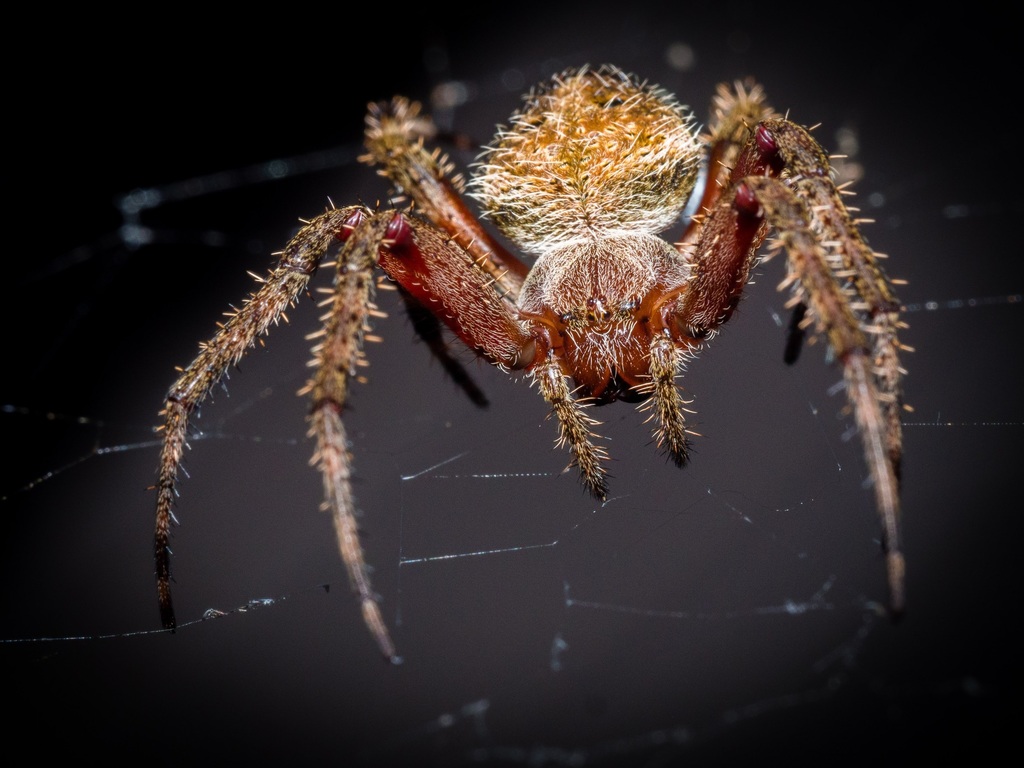
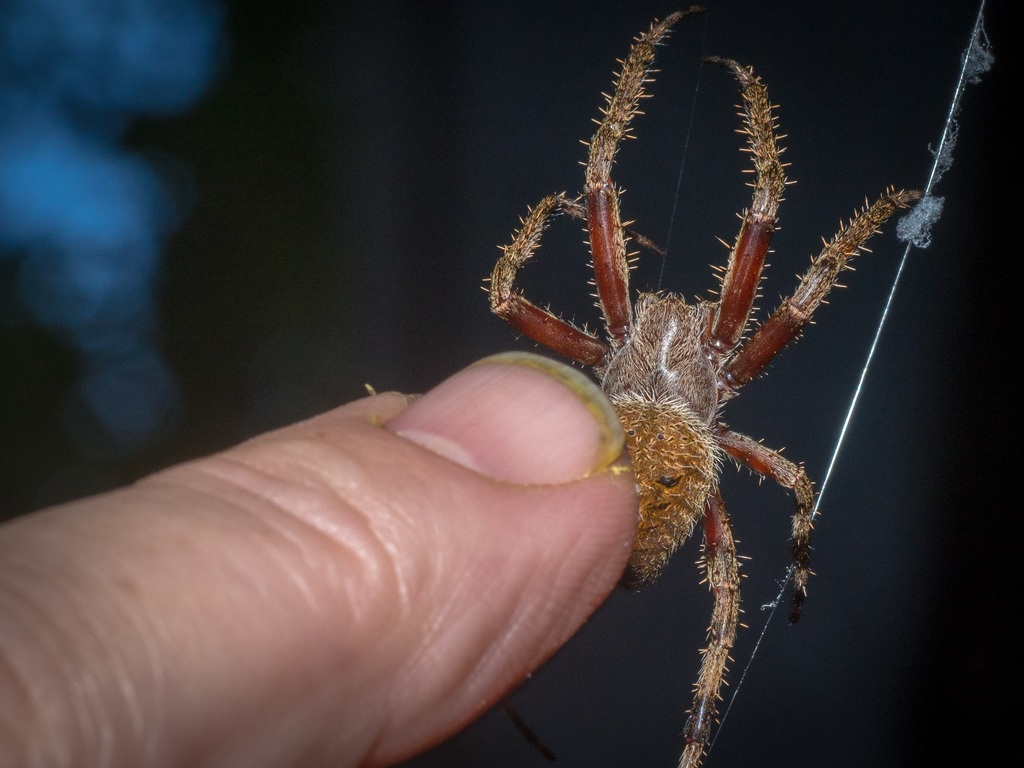
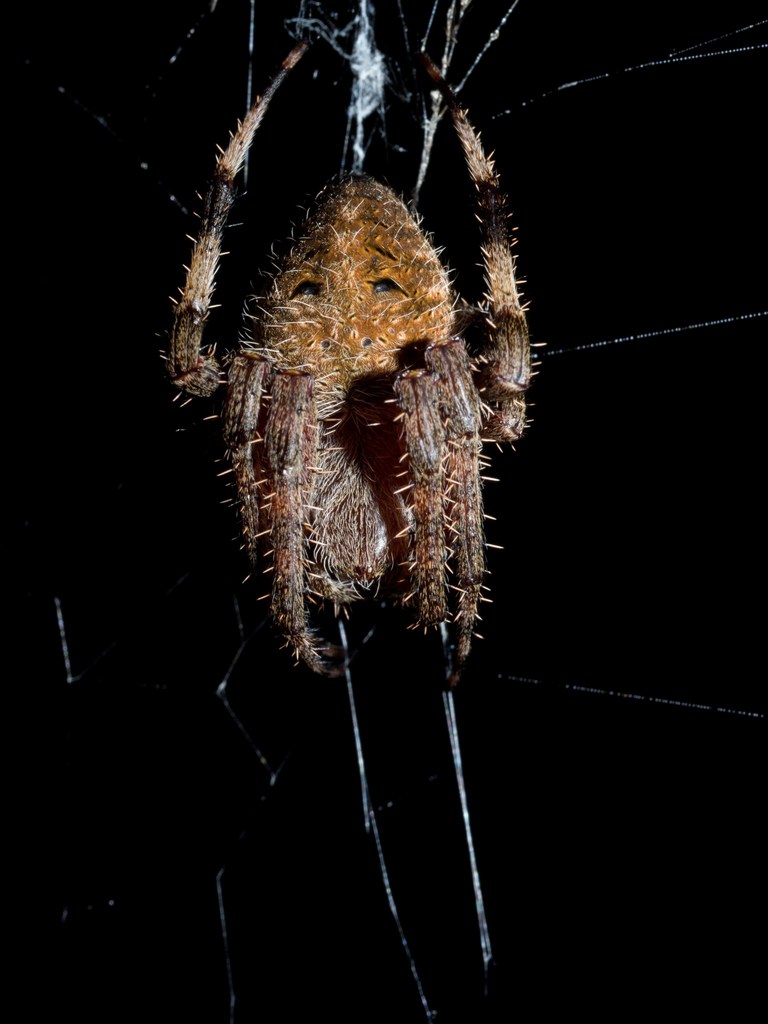




Neoscona crucifera is an orb-weaver spider in the family Araneidae. It is found in the United States from Maine to Florida in the east, to Minnesota in the Midwest, to Arizona in the southwest, southern California coastal communities and in Mexico. Its common names include Hentz orbweaver (after Nicholas Marcellus Hentz), spotted orbweaver, and barn spider. The name \barn spider\ is also commonly used for a different spider, Araneus cavaticus.
Generally nocturnal, females may become diurnal in the fall. Females are about 9.5\u201319 millimeters (0.37\u20130.75\u00a0in) long, while males are somewhat smaller. The upper surface of the abdomen is brown and hairy. The legs display alternating light and dark brown bands. The undersurface of the abdomen is black, with two white spots.
This species is relatively variable in color and sometimes pattern, but is most commonly seen sporting a rusty-red or golden orange color. The orb-shaped web is very large and is often constructed on buildings and other man-made structures, often several feet above ground, especially near outdoor lights. This species is most conspicuous in late summer and early fall.
The orb part of the web may be nearly 2 feet (0.61\u00a0m) in diameter. The eggsac consists of fluffy yellow threads in a rolled leaf over a lenticular or spherical egg mass 5\u201312\u00a0mm (0.20\u20130.47\u00a0in) in diameter, which may contain up to 1,000 eggs. Juveniles are frequently preyed upon by mud daubers. This species will bite if provoked, but its venom is not dangerous to humans.
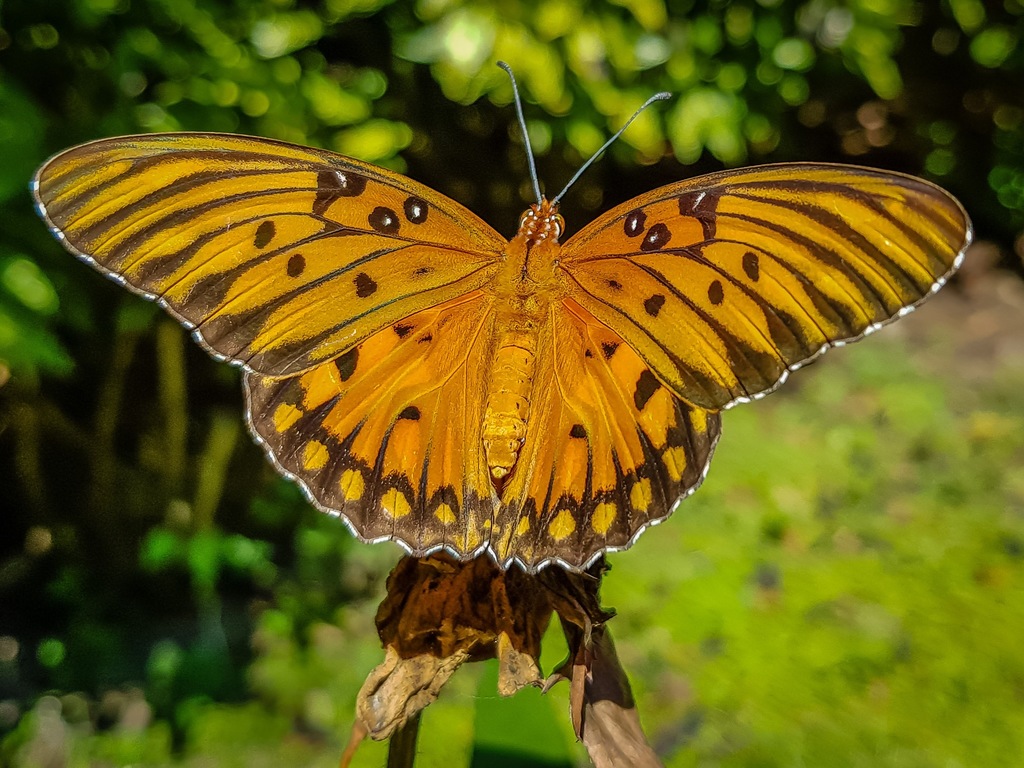

The Gulf fritillary or passion butterfly (Dione vanillae) is a bright orange butterfly in the subfamily Heliconiinae of the family Nymphalidae. That subfamily was formerly set apart as a separate family, the Heliconiidae. The Heliconiinae are \longwing butterflies\, which have long, narrow wings compared to other butterflies.
Dione vanillae is most commonly found in the southern areas of the United States, specifically in many regions of Florida and Texas.
Gulf fritillaries have a chemical defense mechanism in which they release odorous chemicals in response to predator sightings. As a result, common predators learn to avoid this species. Pheromones play a critical role in male-female courtship behaviors, with male gulf fritillaries emitting sex pheromones that contribute to mate choice in females.
The scientific name Papilio vanillae was given to the gulf fritillary by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, based on a 1705 painting by Maria Sibylla Merian (The Metamorphosis of the Insects of Surinam, Plate XXV), which shows the adult and caterpillar of the gulf fritillary on a vanilla orchid, Vanilla planifolia. However, It is now known that the gulf fritillary caterpillar does not use the vanilla plant. The species was moved to the genus Agraulis in 1835 by Boisduval & Le Conte. A phylogenetic analysis reported in 2019 placed Agraulis as a sub-genus of Dione.
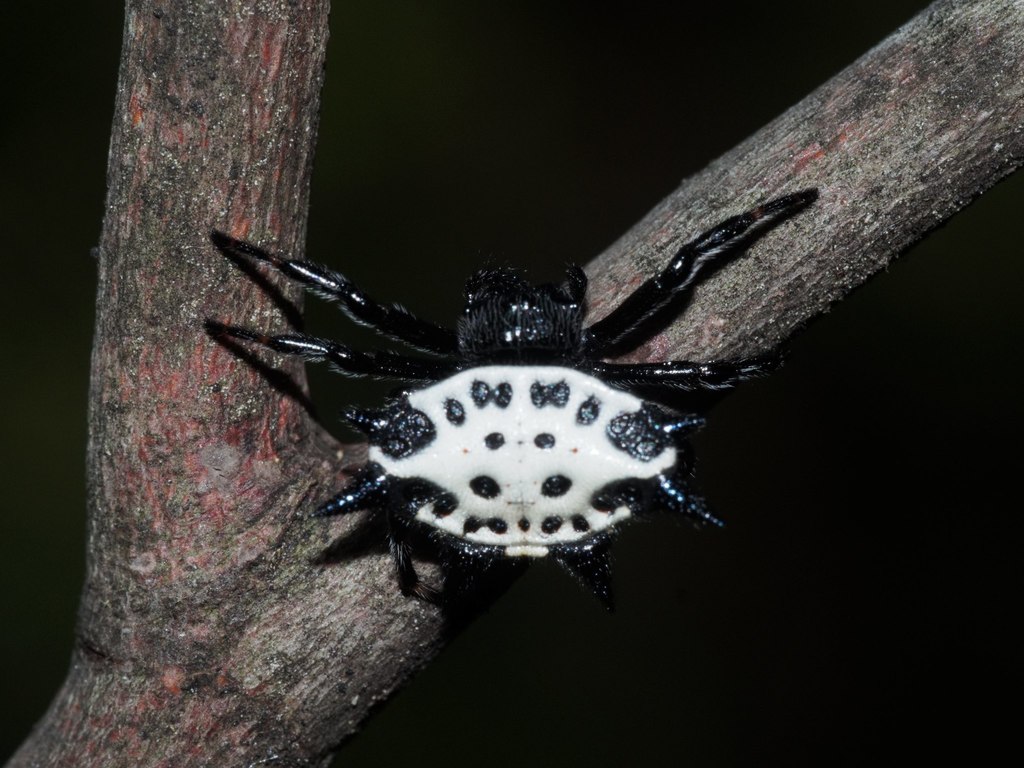
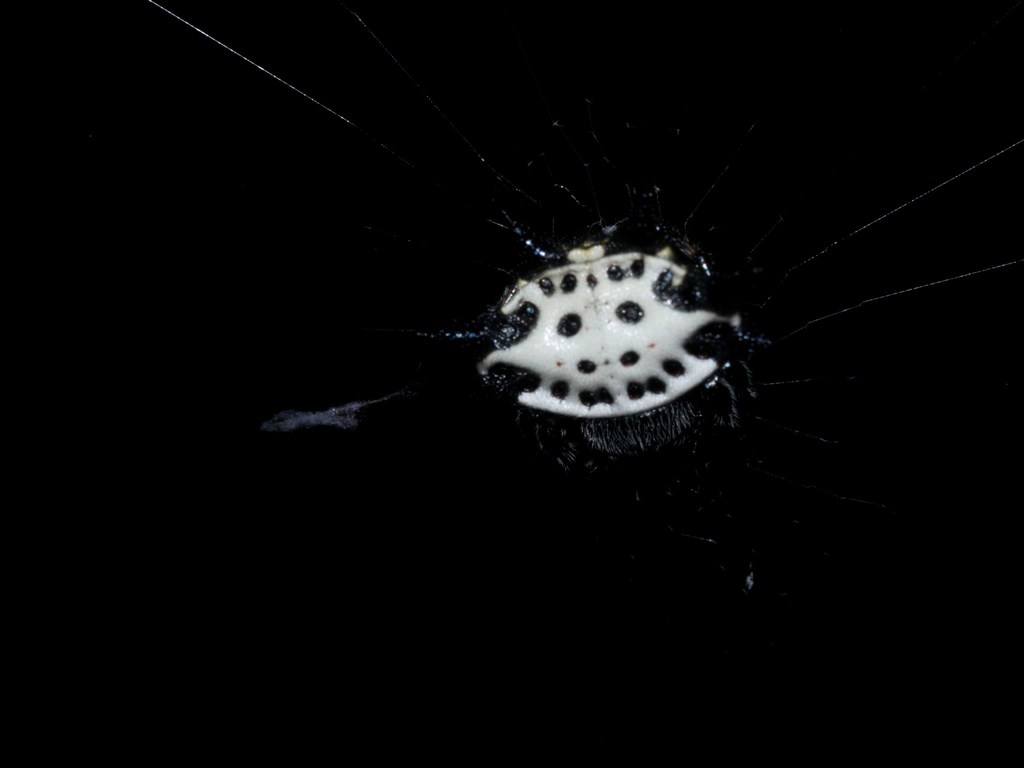



Gasteracantha cancriformis (spinybacked orbweaver) is a species of orb-weaver spider (family Araneidae). It is widely distributed in the New World.
The genus name Gasteracantha derives from the Greek words \u03b3\u03b1\u03c3\u03c4\u03ae\u03c1 (gaster, \belly\) and \u1f04\u03ba\u03b1\u03bd\u03b8\u03b1 (acantha, \thorn\), while the specific epithet cancriformis derives from the Latin words cancer (\crab\) and forma (\shape, form, appearance\).
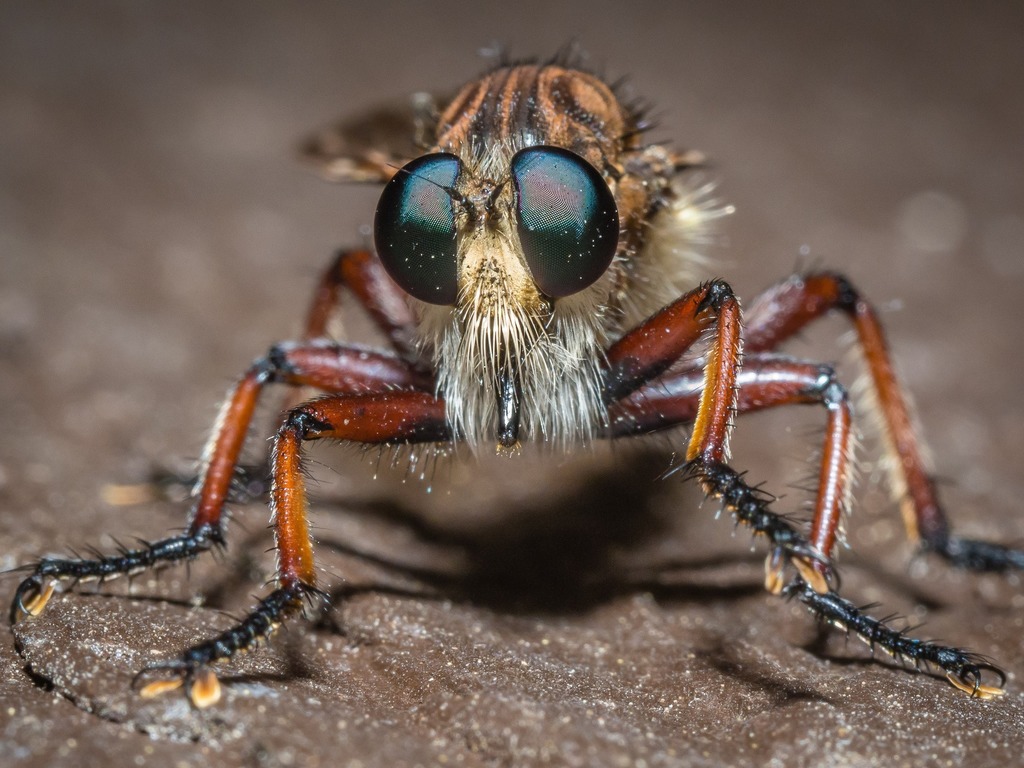


Promachus hinei is a species of robber flies (insects in the family Asilidae).
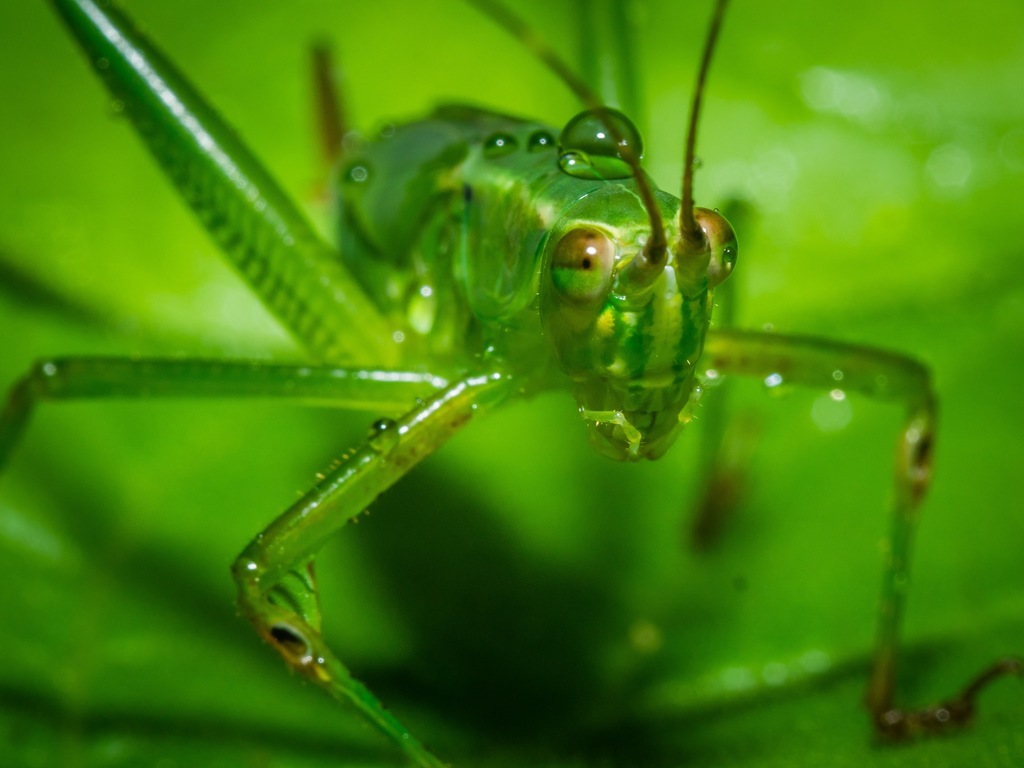
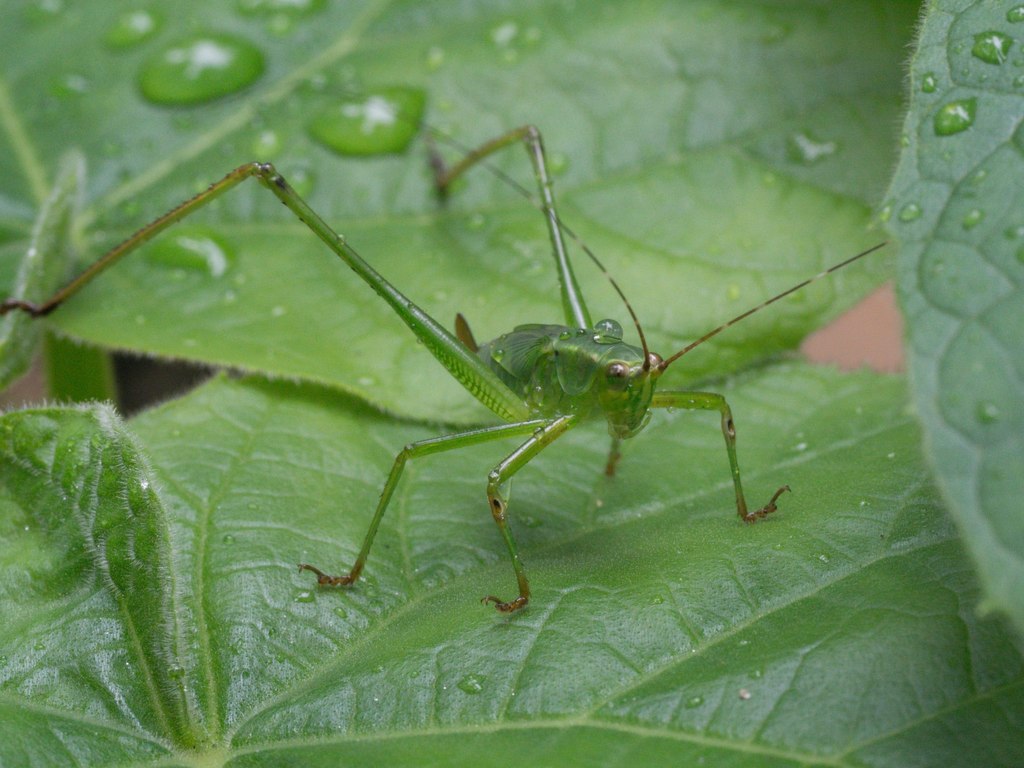



Scudderia is a genus of katydids in the subfamily Phaneropterinae. They are sometimes called bush katydids and are 30-38 mm in length. Their range is most of North America, northernmost being in Southern Canada. They are herbivores, with nymphs feeding primarily on flowers and adults preferring woody deciduous plants.
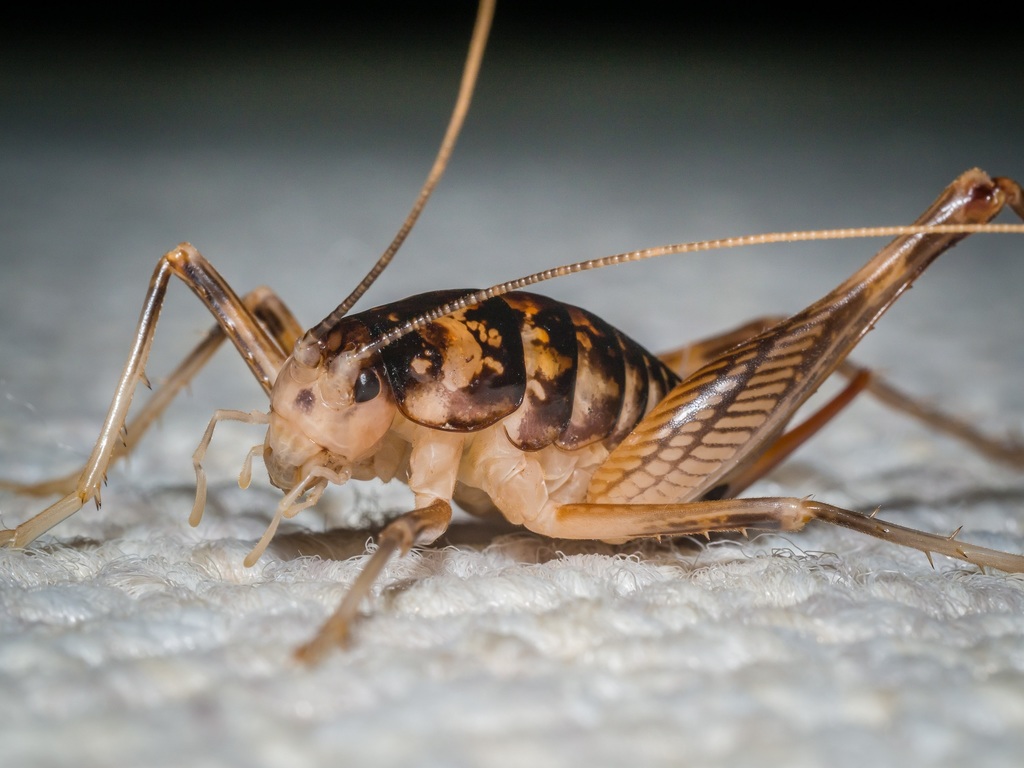


Ceuthophilus is a genus of insects in the cave cricket family Rhaphidophoridae. It contains most of the species that are known commonly as camel crickets.
These insects have thick, dorsally arched bodies. The head is oval in shape with long, tapering antennae. The hind femur is thick and usually spiny in males, and sometimes slightly spiny in females.
Ceuthophilus have varied diets and have been described as omnivores and scavengers. Items observed in the diets of Ceuthophilus species include jelly, tuna, rancid liver, American cheese, pet food, oatmeal, wheat germ, peanut butter, molasses, wild fungi, persimmon, bread, dead and living insects, insect eggs, arachnids, dead bats, dead ring-tailed cats, and human feces.
Species include:
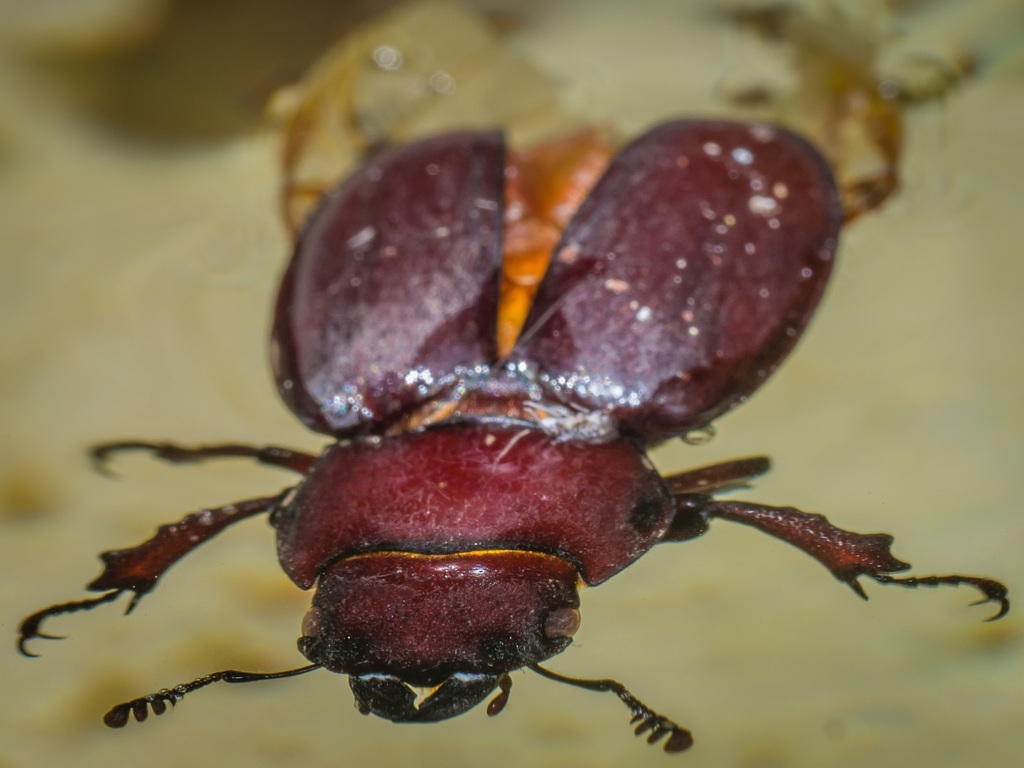
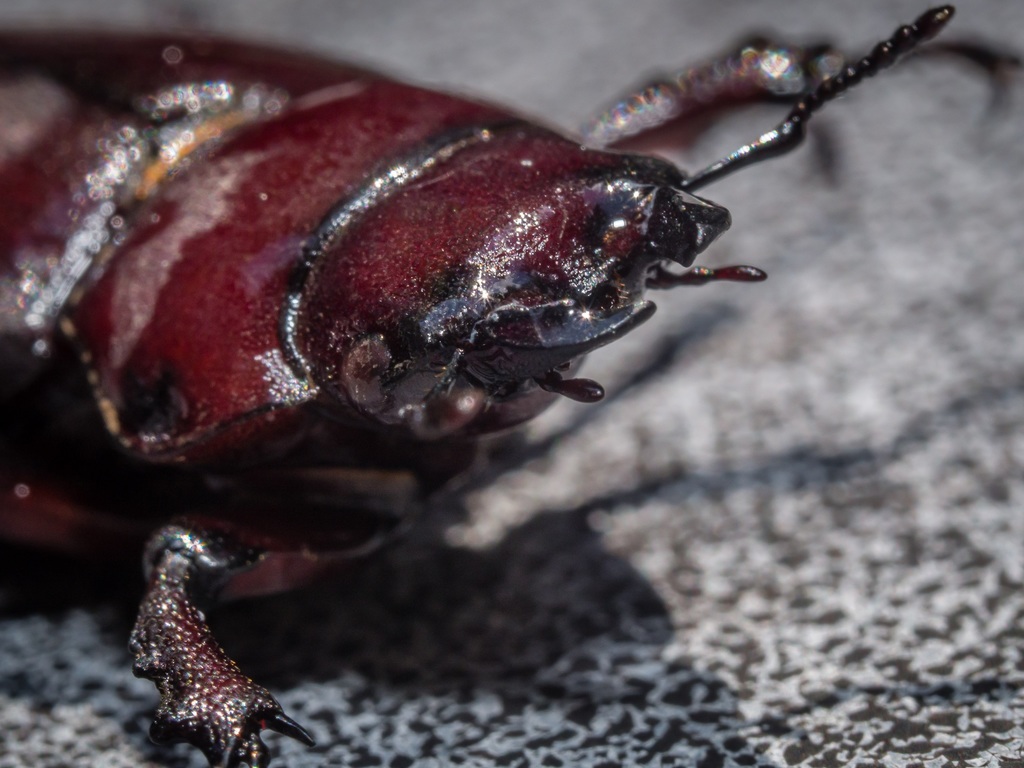



Lucanus capreolus, the reddish-brown stag beetle, is a beetle of the family Lucanidae. The specific name capreolus is derived from Latin, meaning \roe deer\ (capreolus literally means \little goat\). The name refers to the resemblance of the mandibles to deer antlers.
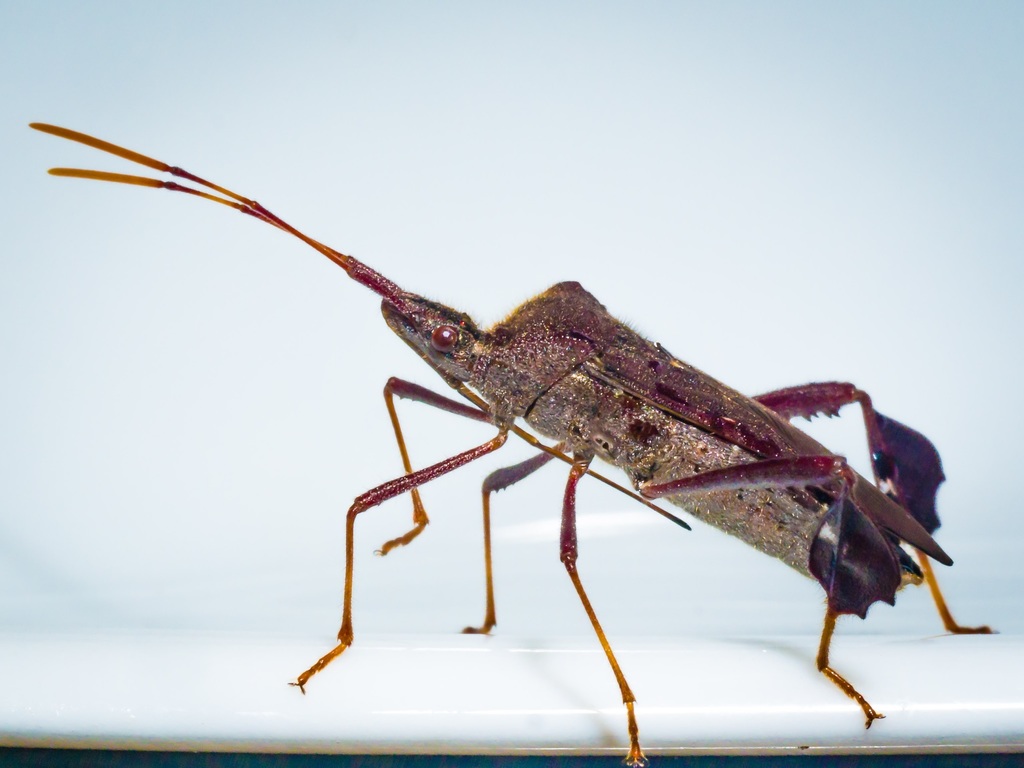
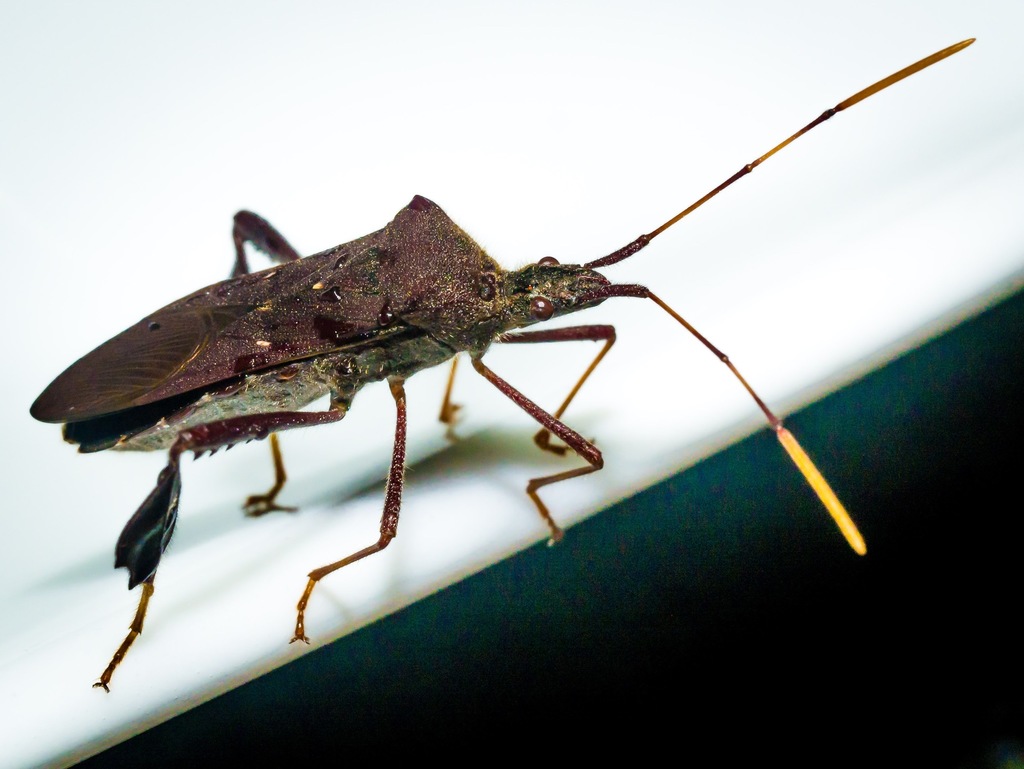



Leptoglossus oppositus a species of leaf-footed bug (family Coreidae) found in North America (also sighted at Northern Nigeria in 2022 by Muhammad U. Jawa). It resembles Leptoglossus fulvicornis but can be distinguished by the deeper scallops in the leaf-like feature of the hind tibia and the addition of three white spots across the hemelytra. This species is widely dispersed from New York to Florida and as far west as Iowa and Minnesota, as well as the southwest regions of the United States into Mexico.
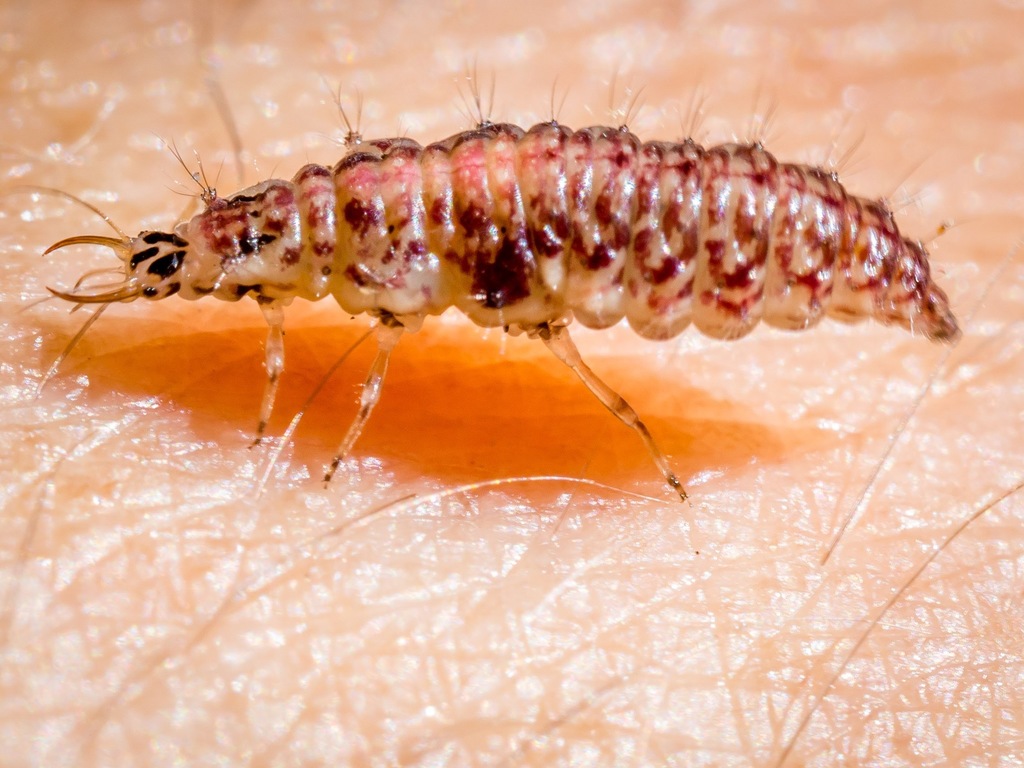
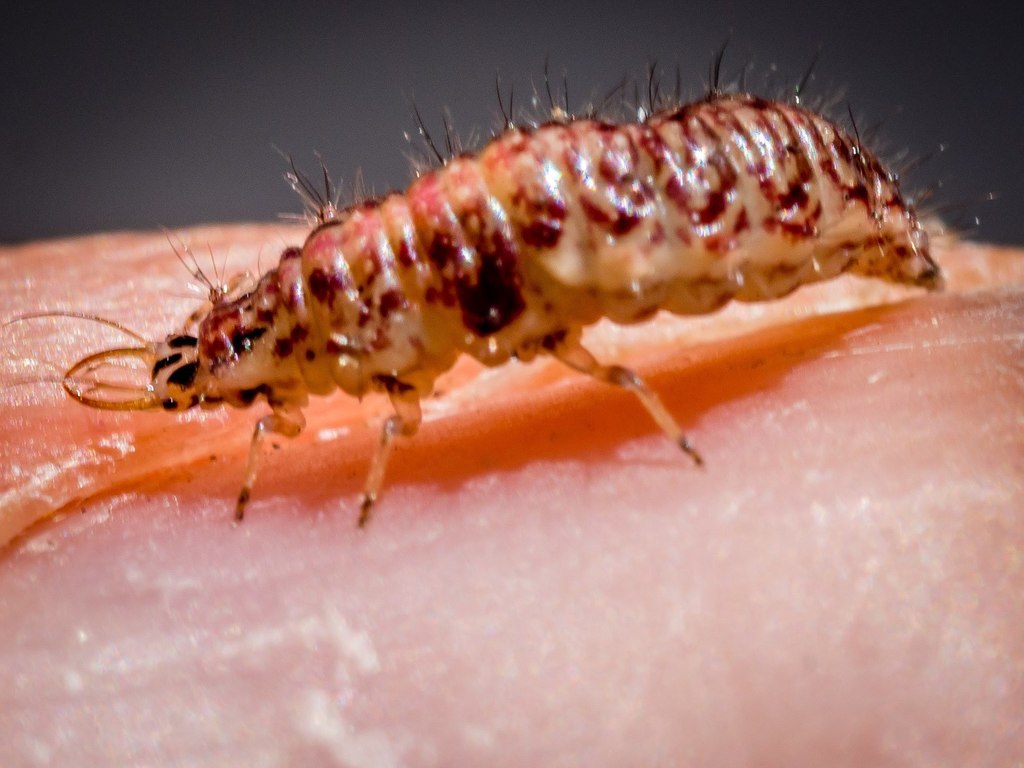
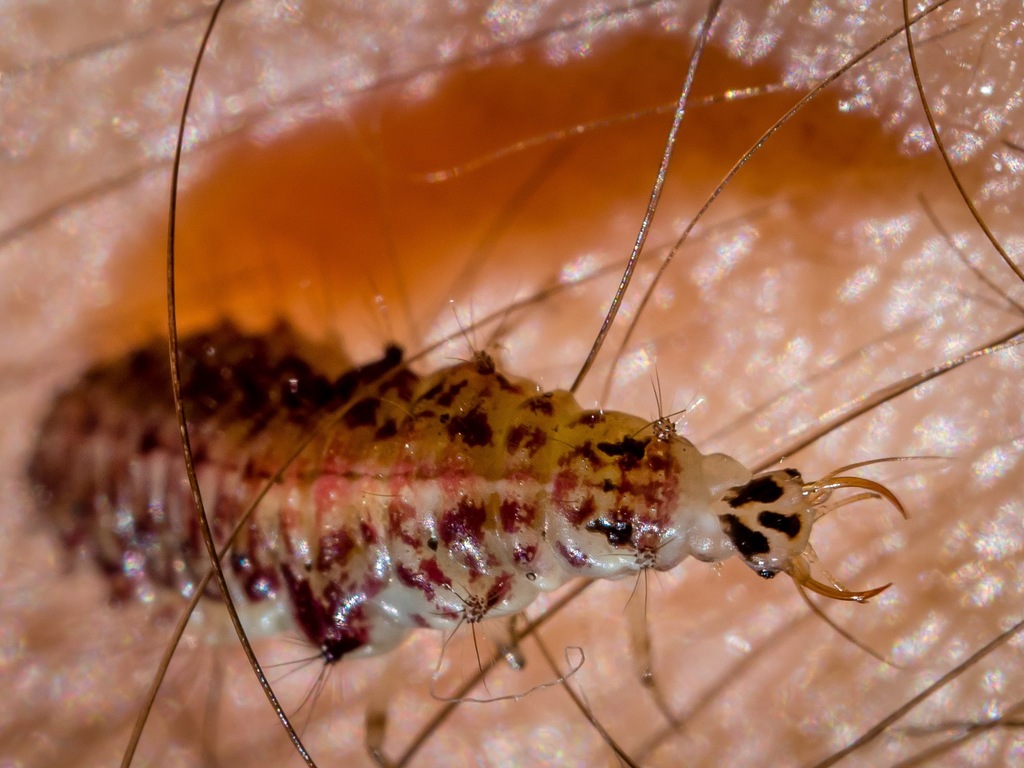


Chrysopa is a genus of green lacewings in the neuropteran family Chrysopidae.
Members of this genus and the genus Chrysoperla are common in much of North America, Europe and Asia. They share similar characteristics and some species have been moved from one genus to the other and back again. Their larvae are predatory and feed on aphids and members of this genus have been used in biological pest control.
William Elford Leach first described this genus in 1815 in Brewster's Edinburgh Encyclop\u00e6dia. Albert Koebele introduced species of Chrysopa to New Zealand in the 1890s, as a method to combat aphids, however no Chrysopa species were able to establish.

Amblyomma americanum, also known as the lone star tick, the northeastern water tick, or the turkey tick, is a type of tick indigenous to much of the eastern United States and Mexico, that bites painlessly and commonly goes unnoticed, remaining attached to its host for as long as seven days until it is fully engorged with blood. It is a member of the phylum Arthropoda, class Arachnida. The adult lone star tick is sexually dimorphic, named for a silvery-white, star-shaped spot or \lone star\ present near the center of the posterior portion of the adult female shield (scutum); adult males conversely have varied white streaks or spots around the margins of their shields.
A. americanum is also referred to as the turkey tick in some Midwestern U.S. states, where wild turkeys are a common host for immature ticks. It is the primary vector of Ehrlichia chaffeensis, which causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis, and Ehrlichia ewingii, which causes human and canine granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Other disease-causing bacterial agents isolated from lone star ticks include Francisella tularensis, Rickettsia amblyommii, and Coxiella burnetti.
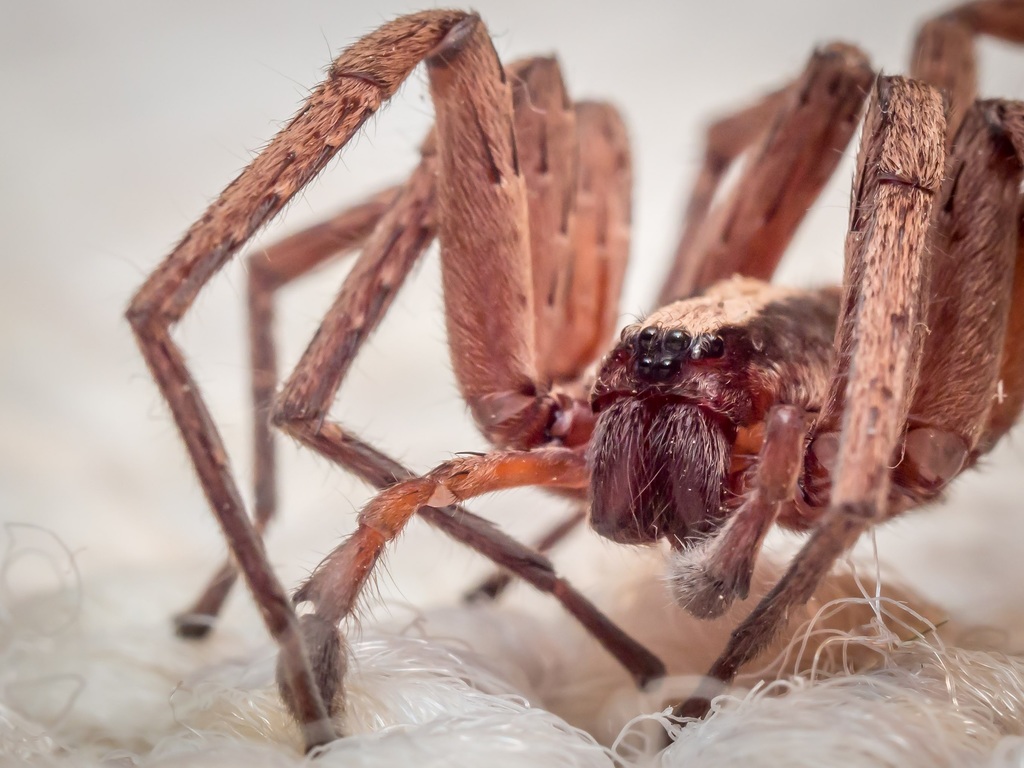
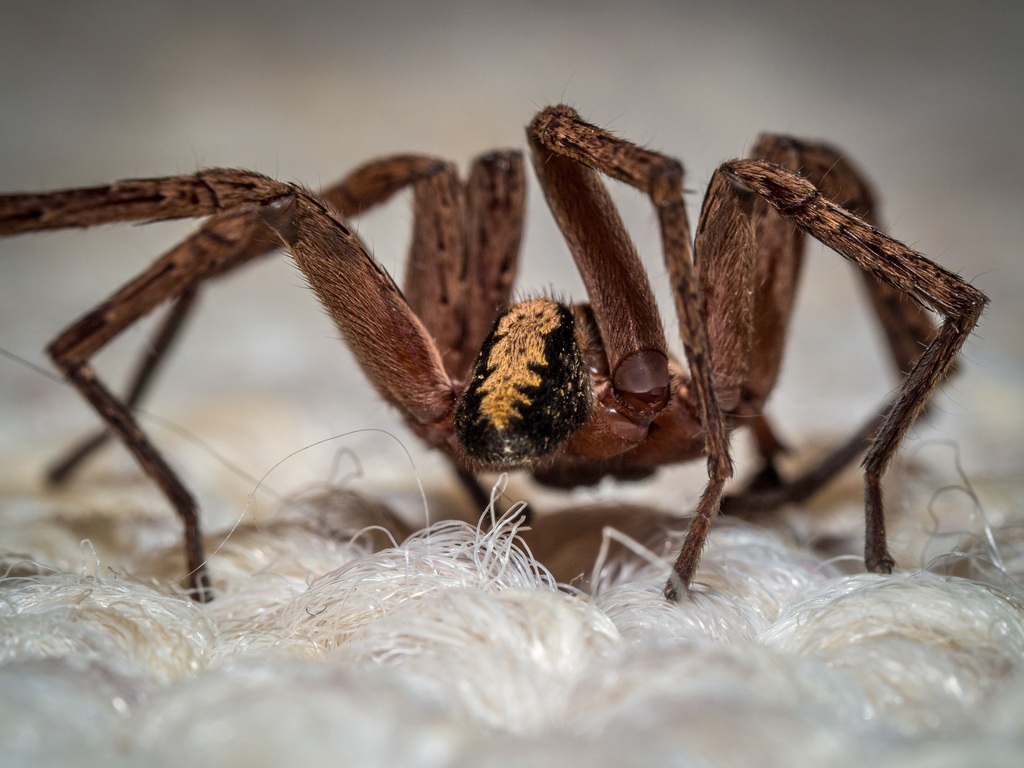



Lycosoidea is a clade or superfamily of araneomorph spiders. The traditional circumscription was based on a feature of the eyes. The tapetum is a reflective layer at the back of the eye, thought to increase sensitivity in low light levels. Lycosoids were then defined by having a \grate-shaped\ tapetum. Research from the late 1990s onwards suggests that this feature has evolved more than once, possibly as many as five times, so that the original Lycosoidea is paraphyletic. Studies published in 2014 and 2015 suggest that a smaller group of families does form a clade.
The reflective attributes of the tapeta vary significantly betwixt lycosoid spiders.
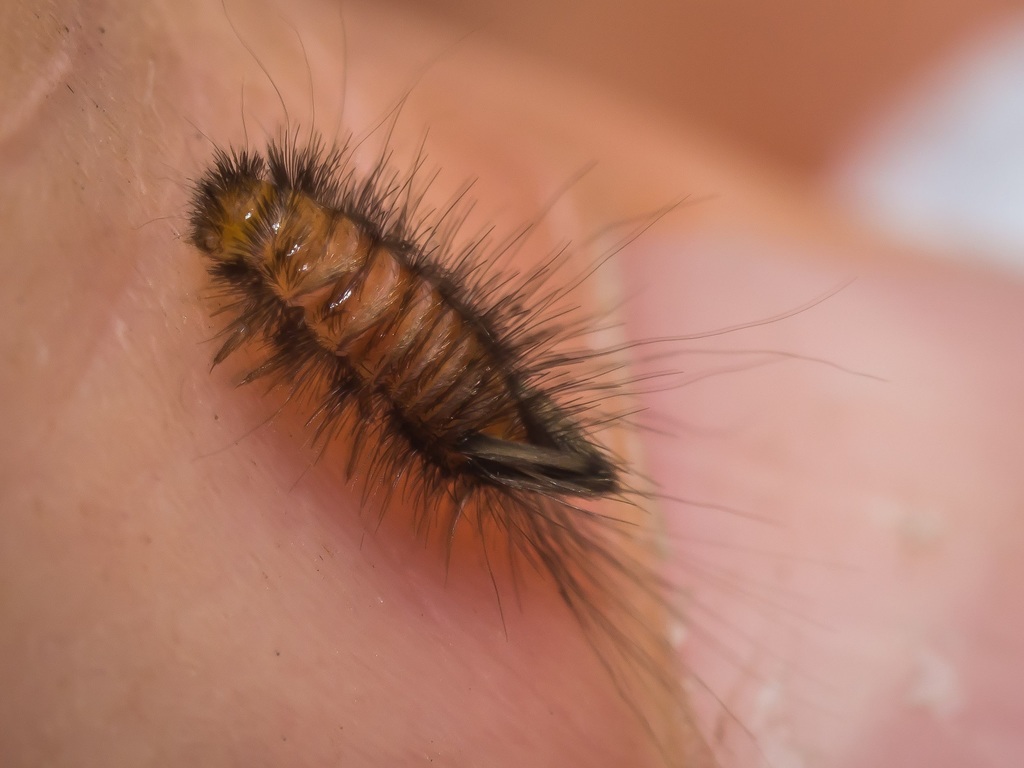
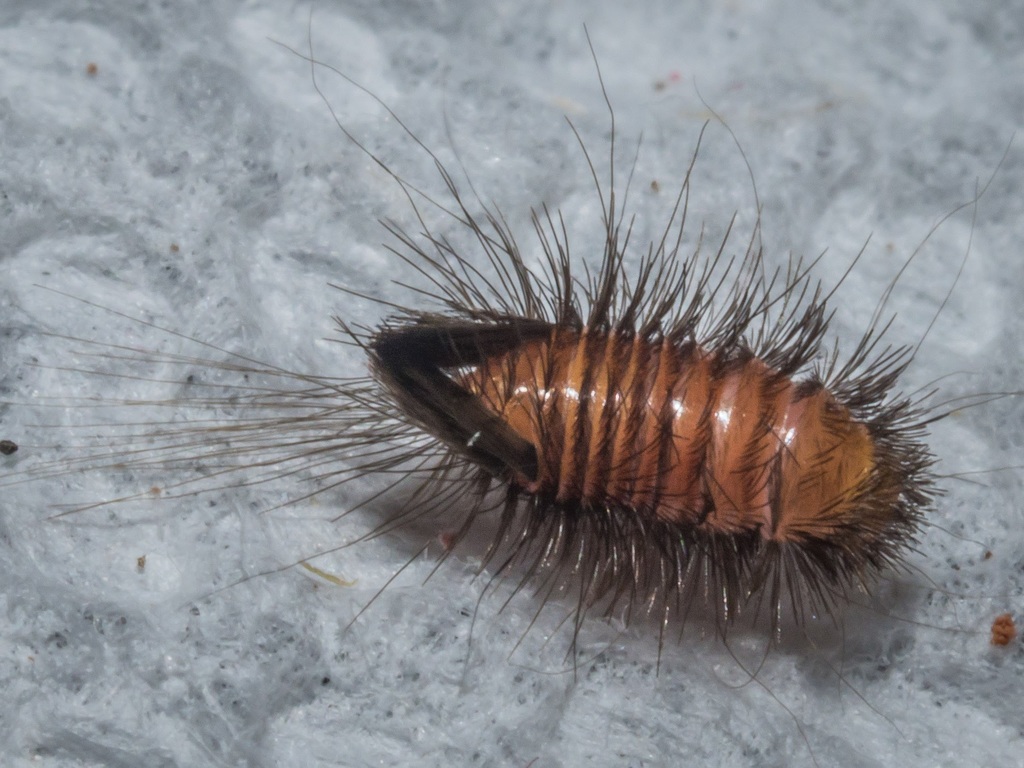
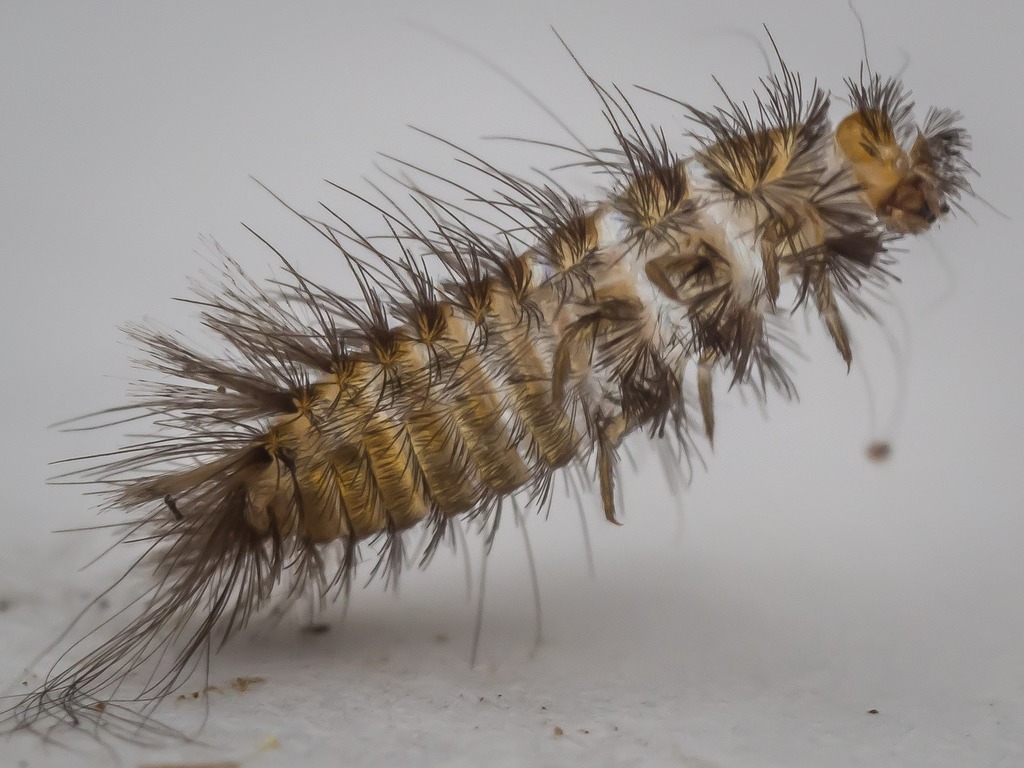



Tineola bisselliella, known as the common clothes moth, webbing clothes moth, or simply clothing moth, is a species of fungus moth (family Tineidae, subfamily Tineinae). It is the type species of its genus Tineola and was first described by the Swedish entomologist Arvid David Hummel in 1823. The specific name is commonly misspelled biselliella \u2013 for example by G. A. W. Herrich-Sch\u00e4ffer, when he established Tineola in 1853.
The larvae (caterpillars) of this moth are considered a serious pest, as they can derive nourishment from clothing \u2013 in particular wool, but many other natural fibres \u2013 and also, like most related species, from stored foods, such as grains.

Muscidae are a family of flies found in the superfamily Muscoidea.
Muscidae, some of which are commonly known as house flies or stable flies due to their synanthropy, are worldwide in distribution and contain almost 4,000 described species in over 100 genera.
Most species are not synanthropic. Adults can be predatory, hematophagous, saprophagous, or feed on a number of types of plant and animal exudates. They can be attracted to various substances including sugar, sweat, tears [1] and blood. Larvae occur in various habitats including decaying vegetation, dry and wet soil, nests of insects and birds, fresh water, and carrion.
The housefly, Musca domestica, is the best known and most important species.
Some, from the genera Hydrotaea and Muscina, are involved in forensic case studies.

Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek \u03b4\u03b9- di- \two\, and \u03c0\u03c4\u03b5\u03c1\u03cc\u03bd pteron \wing\. Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described.
Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the larval food-source and the larvae, which lack true limbs, develop in a protected environment, often inside their food source. Other species like Metopia argyrocephala are ovoviviparous, opportunistically depositing hatched or hatching maggots instead of eggs on carrion, dung, decaying material, or open wounds of mammals. The pupa is a tough capsule from which the adult emerges when ready to do so; flies mostly have short lives as adults.
Diptera is one of the major insect orders and of considerable ecological and human importance. Flies are important pollinators, second only to the bees and their Hymenopteran relatives. Flies may have been among the evolutionarily earliest pollinators responsible for early plant pollination. Fruit flies are used as model organisms in research, but less benignly, mosquitoes are vectors for malaria, dengue, West Nile fever, yellow fever, encephalitis, and other infectious diseases; and houseflies, commensal with humans all over the world, spread food-borne illnesses. Flies can be annoyances especially in some parts of the world where they can occur in large numbers, buzzing and settling on the skin or eyes to bite or seek fluids. Larger flies such as tsetse flies and screwworms cause significant economic harm to cattle. Blowfly larvae, known as gentles, and other dipteran larvae, known more generally as maggots, are used as fishing bait and as food for carnivorous animals. They are also used in medicine in debridement to clean wounds.
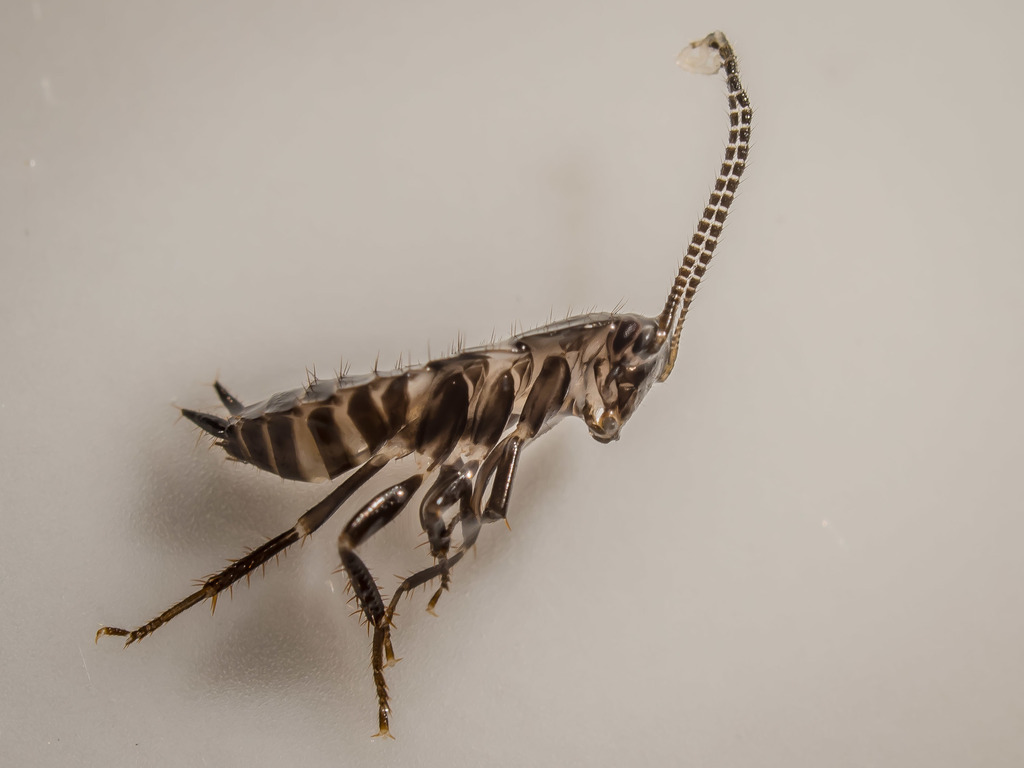

Blattodea is an order of insects that contains cockroaches and termites. Formerly, termites were considered a separate order, Isoptera, but genetic and molecular evidence suggests they evolved from within the cockroach lineage, cladistically making them cockroaches as well. The Blattodea and the mantis (order Mantodea) are now all considered part of the superorder Dictyoptera. Blattodea includes approximately 4,400 species of cockroach in almost 500 genera, and about 3,000 species of termite in around 300 genera.
Termites are pale-coloured, soft-bodied eusocial insects that live in colonies, whereas cockroaches are darker-coloured (often brown), sclerotized, segmented insects. Within the colony, termites have a caste system, with a pair of mature reproductives, the king and the queen, and numerous sterile workers and soldiers. Cockroaches are not colonial but do have a tendency to aggregate and may be considered pre-social, as all adults are capable of breeding. Other similarities between the two groups include various social behaviours, trail following, kin recognition, and methods of communication.
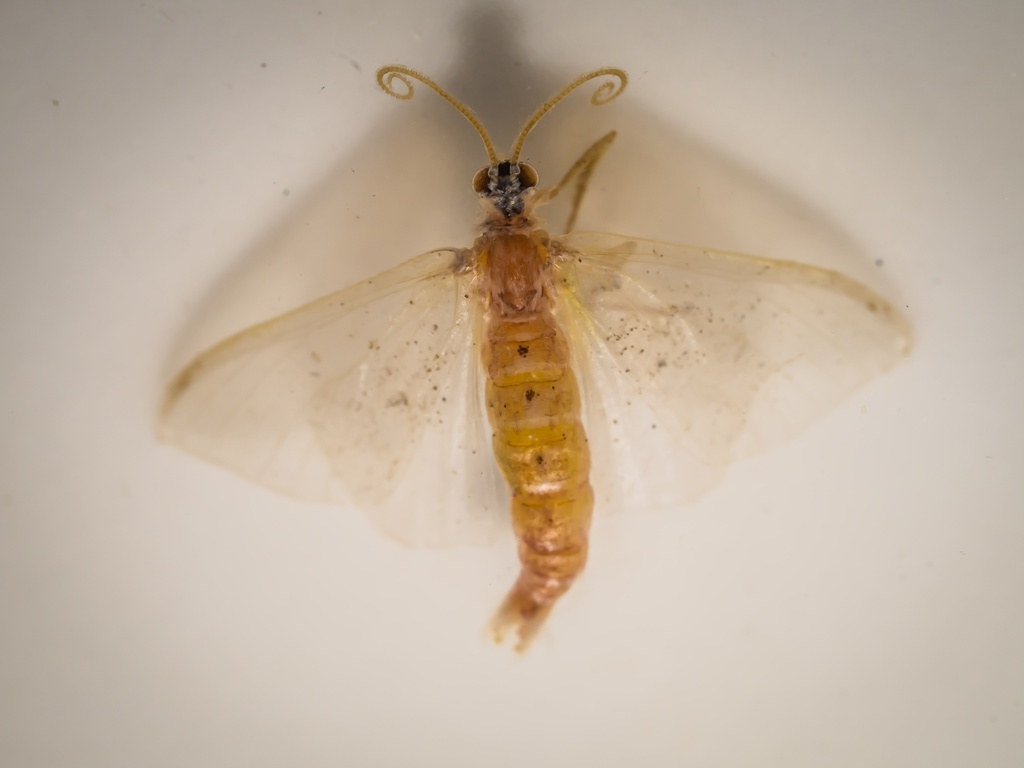

Lepidoptera ( LEP-ih-DOP-t\u0259r-\u0259) is an order of insects that includes butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 families and 46 superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most species-rich orders, along with the Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera.
Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scales that cover the bodies, wings, and a proboscis. The scales are modified, flattened \hairs\, and give butterflies and moths their wide variety of colors and patterns. Almost all species have some form of membranous wings, except for a few that have reduced wings or are wingless. Mating and the laying of eggs is normally performed near or on host plants for the larvae. Like most other insects, butterflies and moths are holometabolous, meaning they undergo complete metamorphosis. The larvae are commonly called caterpillars, and are completely different from their adult moth or butterfly forms, having a cylindrical body with a well-developed head, mandible mouth parts, three pairs of thoracic legs and from none up to five pairs of prolegs. As they grow, these larvae change in appearance, going through a series of stages called instars. Once fully matured, the larva develops into a pupa. A few butterflies and many moth species spin a silk case or cocoon prior to pupating, while others do not, instead going underground. A butterfly pupa, called a chrysalis, has a hard skin, usually with no cocoon. Once the pupa has completed its metamorphosis, a sexually mature adult emerges.
The Lepidoptera have, over millions of years, evolved a wide range of wing patterns and coloration ranging from drab moths akin to the related order Trichoptera, to the brightly colored and complex-patterned butterflies. Accordingly, this is the most recognized and popular of insect orders with many people involved in the observation, study, collection, rearing of, and commerce in these insects. A person who collects or studies this order is referred to as a lepidopterist.
Butterflies and moths play an important role in the natural ecosystem as pollinators and as food in the food chain; conversely, their larvae are considered very problematic to vegetation in agriculture, as their main source of food is often live plant matter. In many species, the female may produce from 200 to 600 eggs, while in others, the number may approach 30,000 eggs in one day. The caterpillars hatching from these eggs can cause damage to large quantities of crops. Many moth and butterfly species are of economic interest by virtue of their role as pollinators, the silk they produce, or as pest species.
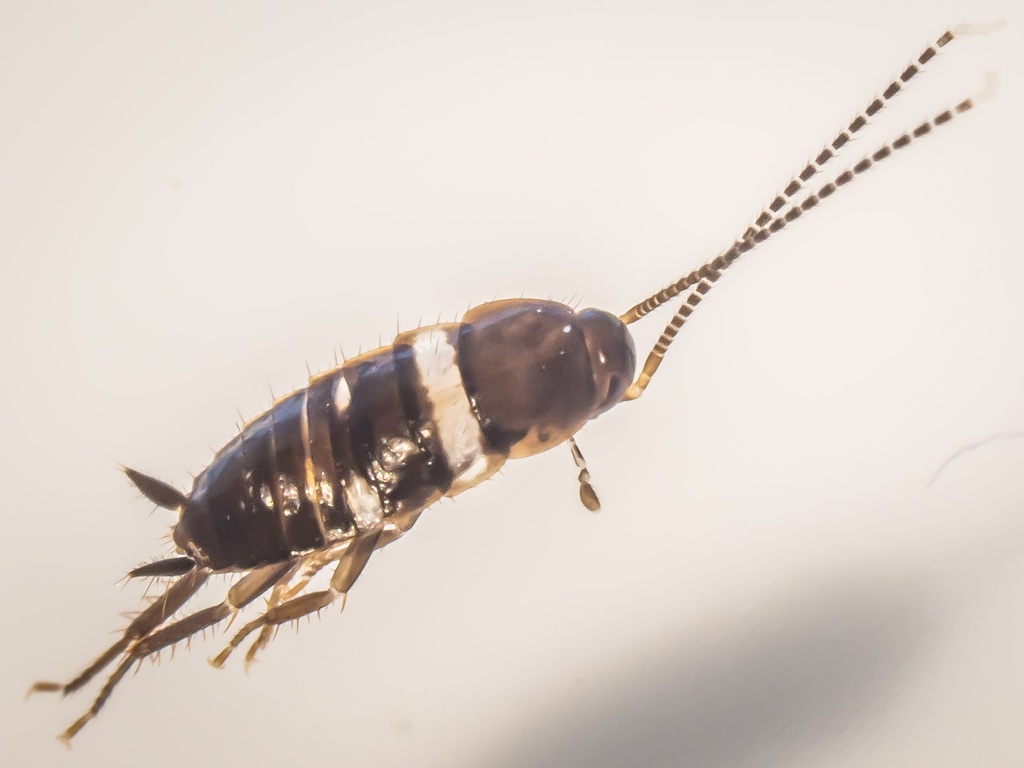
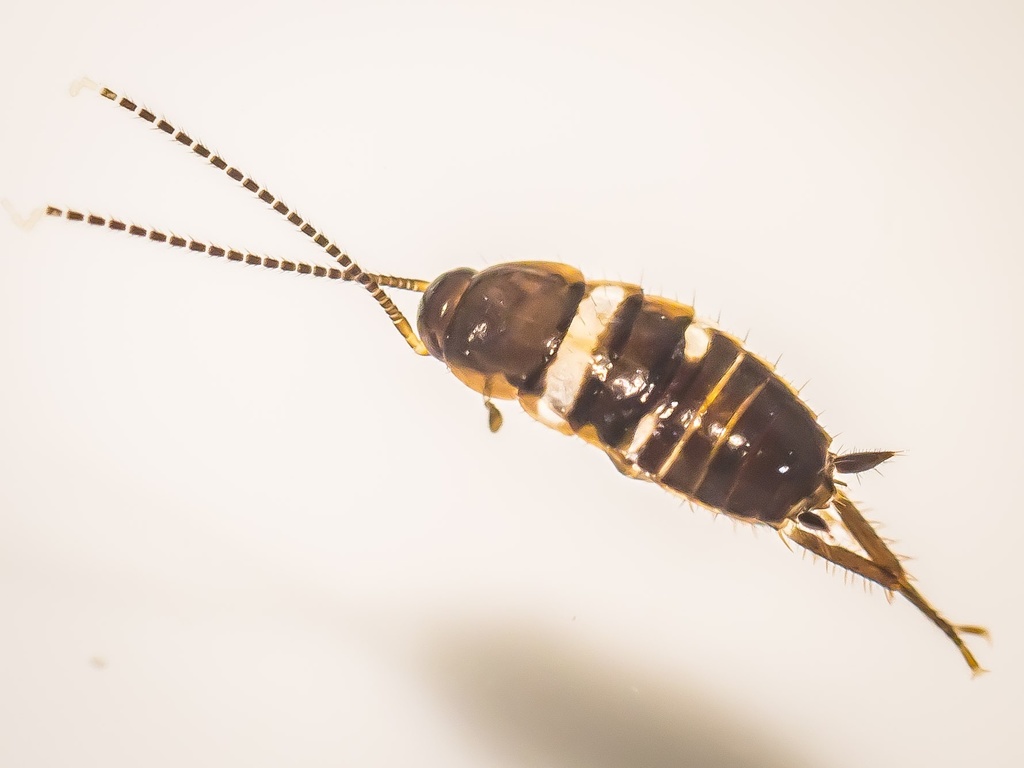


Periplaneta is a genus of cockroaches.
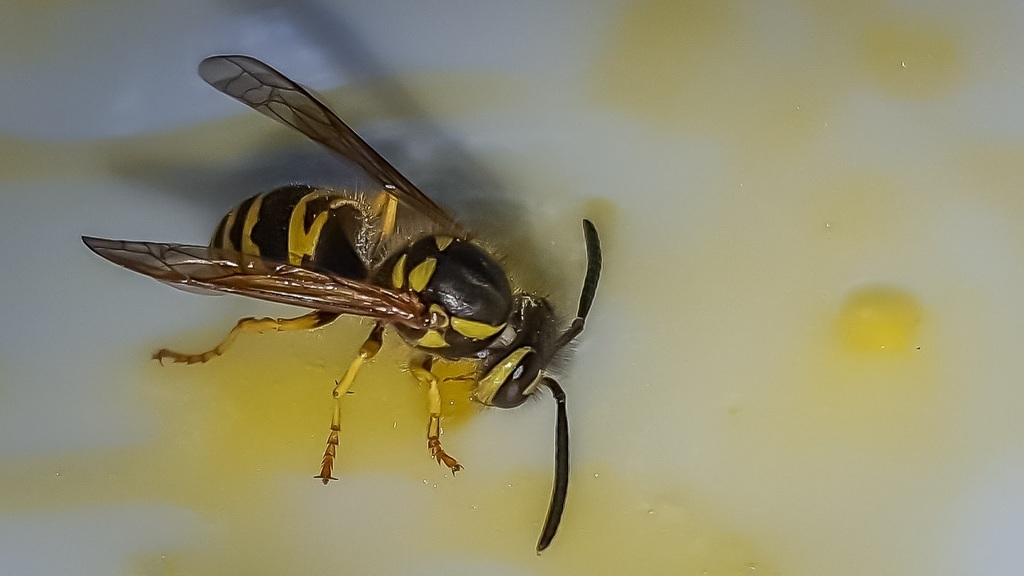

The eastern yellow jacket or eastern yellowjacket (Vespula maculifrons) is a wasp found in eastern North America. Although most of their nests are subterranean, they are often considered a pest due to their nesting in recreational areas and buildings. This yellow jacket is a social insect, living in colonies of hundreds to thousands of individuals. Along with their subfamily, Vespinae, this species demonstrates supportive parental care for offspring, separation of reproductive and sterile castes, and overlapping generations. They aggressively defend their hives from threats and are known to inflict painful stings.
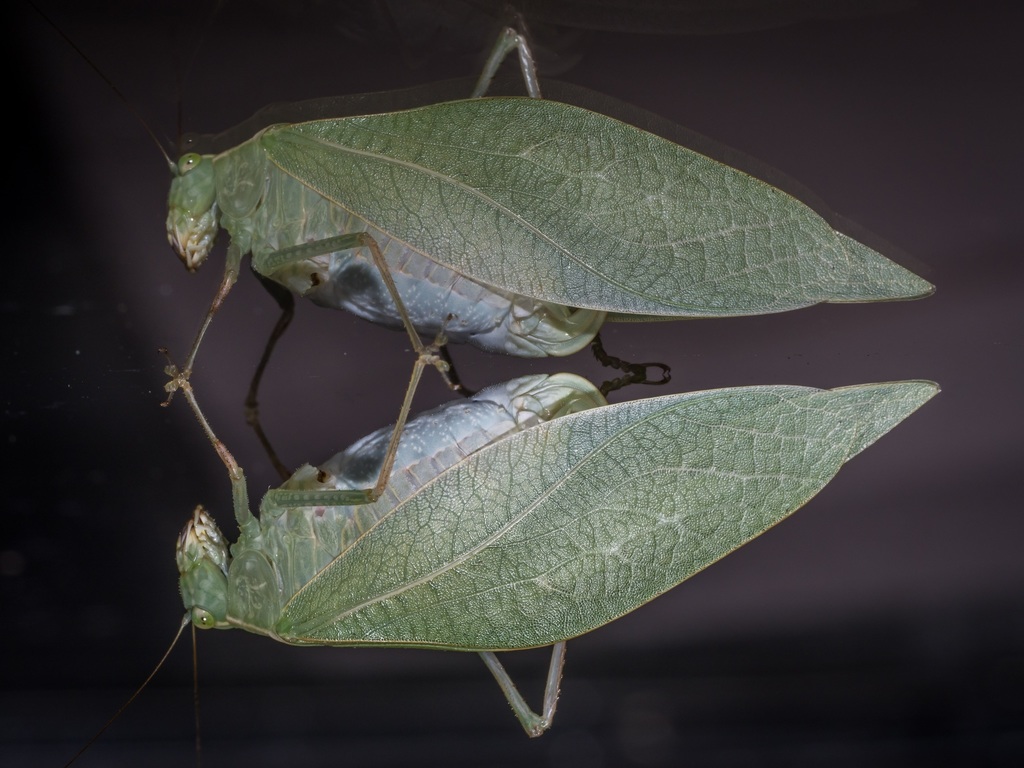


Microcentrum rhombifolium is a species of insect in the family Tettigoniidae. Common names include greater angle-wing katydid, broad-winged katydid, and angular-winged katydid. They live across North America in trees and shrubs. Adults reach 50-65 mm in length and are rhombus-shaped. Their green coloration mimics leaves. Adults are active in late summer and autumn and have a \ticking\ call.

Antheraea polyphemus, the Polyphemus moth, is a North American member of the family Saturniidae, the giant silk moths. It is a tan-colored moth, with an average wingspan of 15\u00a0cm (6\u00a0in). The most notable feature of the moth is its large, purplish eyespots on its two hindwings. The eyespots give it its name \u2013 from the Greek myth of the cyclops Polyphemus. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1776. The species is widespread in continental North America, with local populations found throughout subarctic Canada and the United States. The caterpillar can eat 86,000 times its weight at emergence in a little less than two months. Polyphemus moths are considered to be very polyphagous, meaning they eat from a wide variety of plants
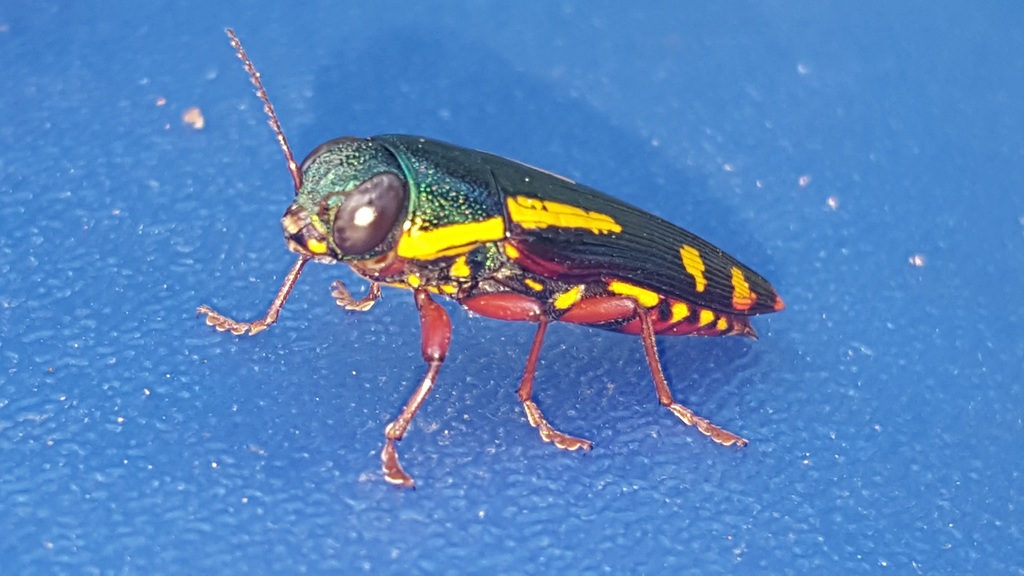


Buprestis rufipes, the red-legged buprestis, is a green metallic wood boring beetle native to southern and eastern United States in North America. Little is known about this beetle. It apparently inhabits dead or dying hardwood in its adult phase.
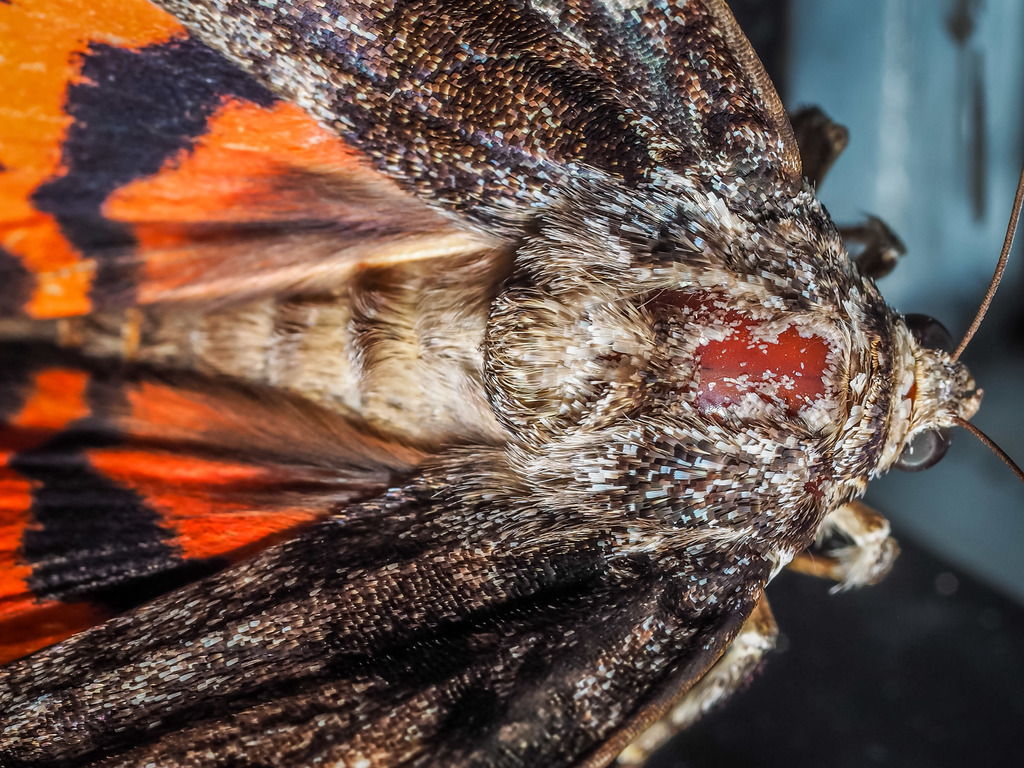
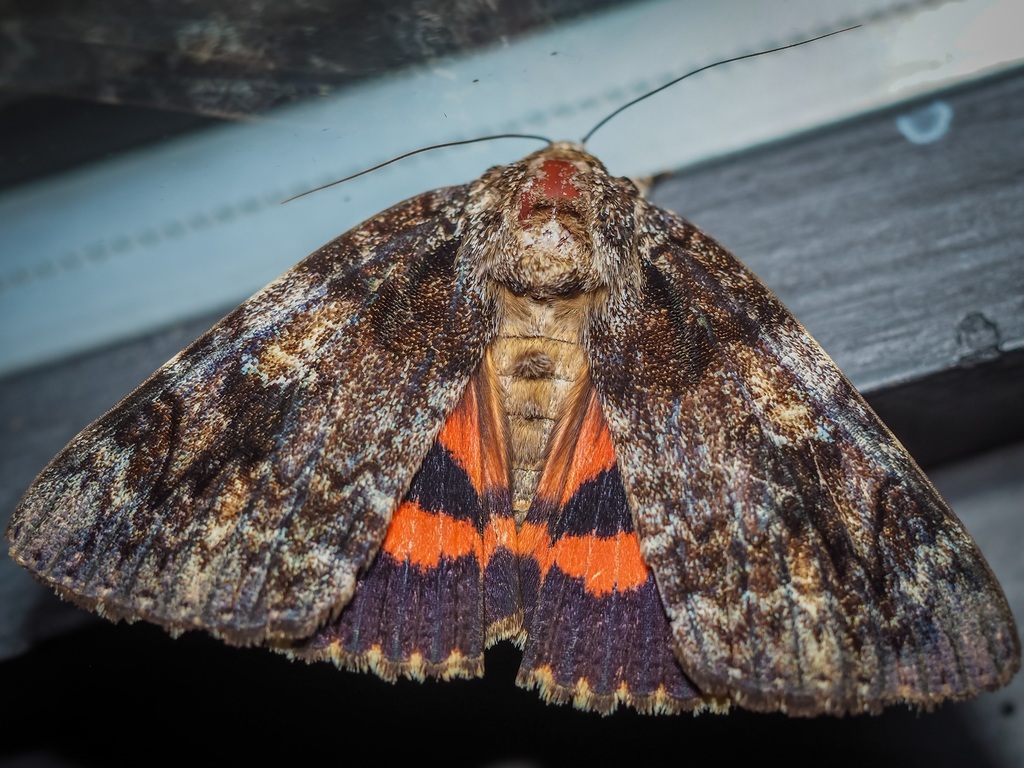
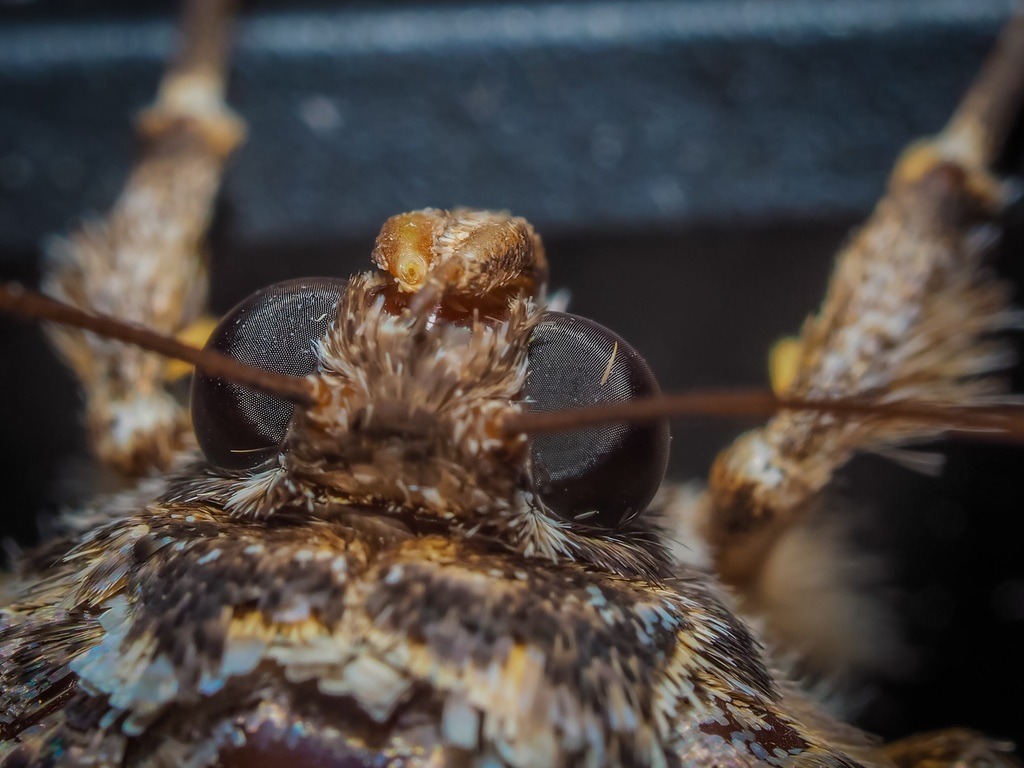



Catocala ilia, the Ilia underwing, beloved underwing or wife underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1776. It can be found in the eastern part of the United States as well as southern Canada. Subspecies Catocala ilia zoe can be found in California and Arizona.
The wingspan is 65\u201382\u00a0mm. A spot on its forewing with a distinct white circle which encompasses it distinguishes this moth from others in the same family. Otherwise, the forewing can be extremely variable. The underwing that it is named for can range in color from light orange to a deep red. The moths flies from June to September depending on the location.
The larvae feed on oak, including black, burr, red, and white oaks.
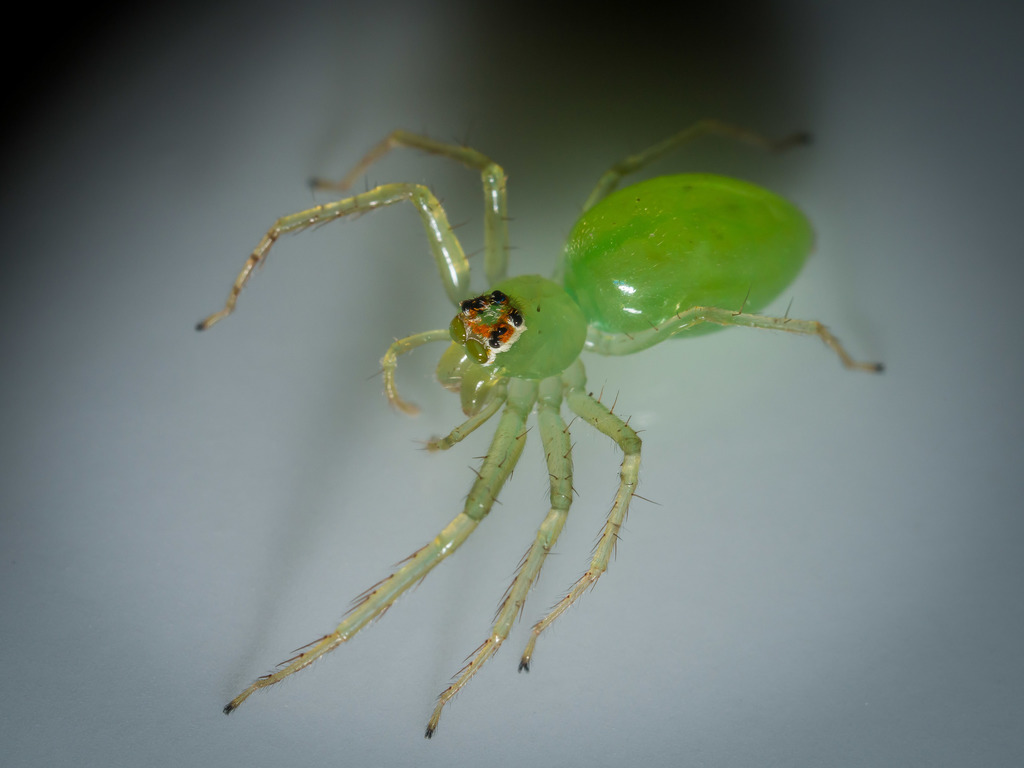

Lyssomanes viridis, commonly known as the magnolia green jumper, is a species of jumping spider of the genus Lyssomanes, for which it is the type species. The species is native to the United States, being found in much of the Southeastern United States as far north as Pennsylvania and down into parts of Texas.
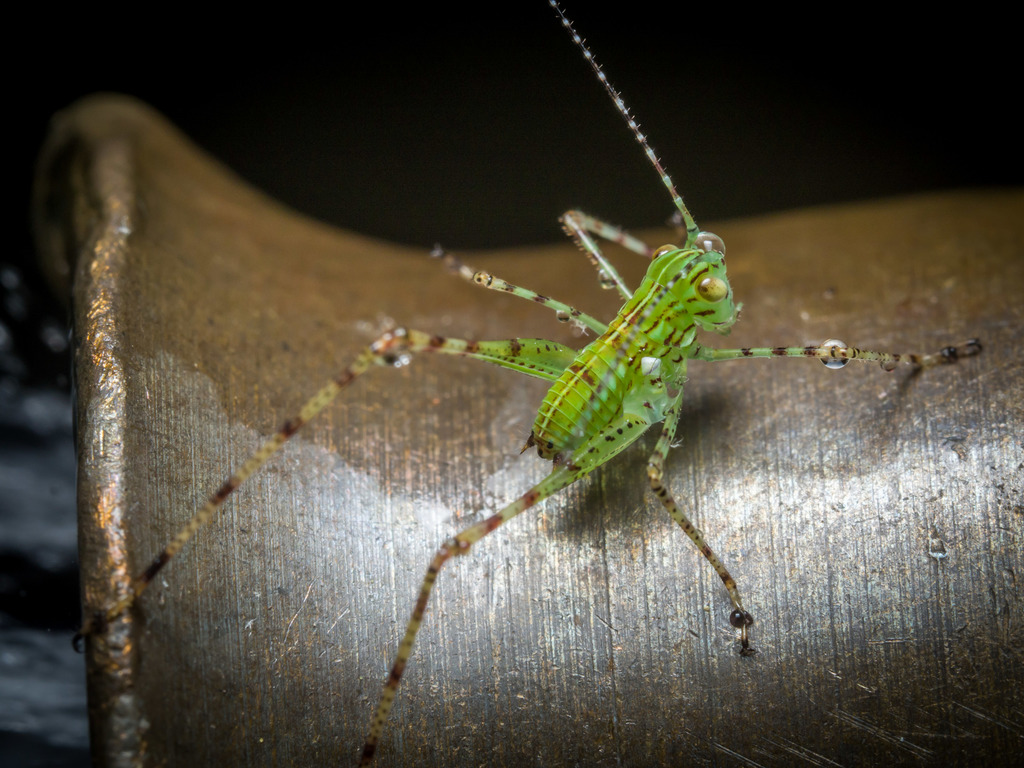
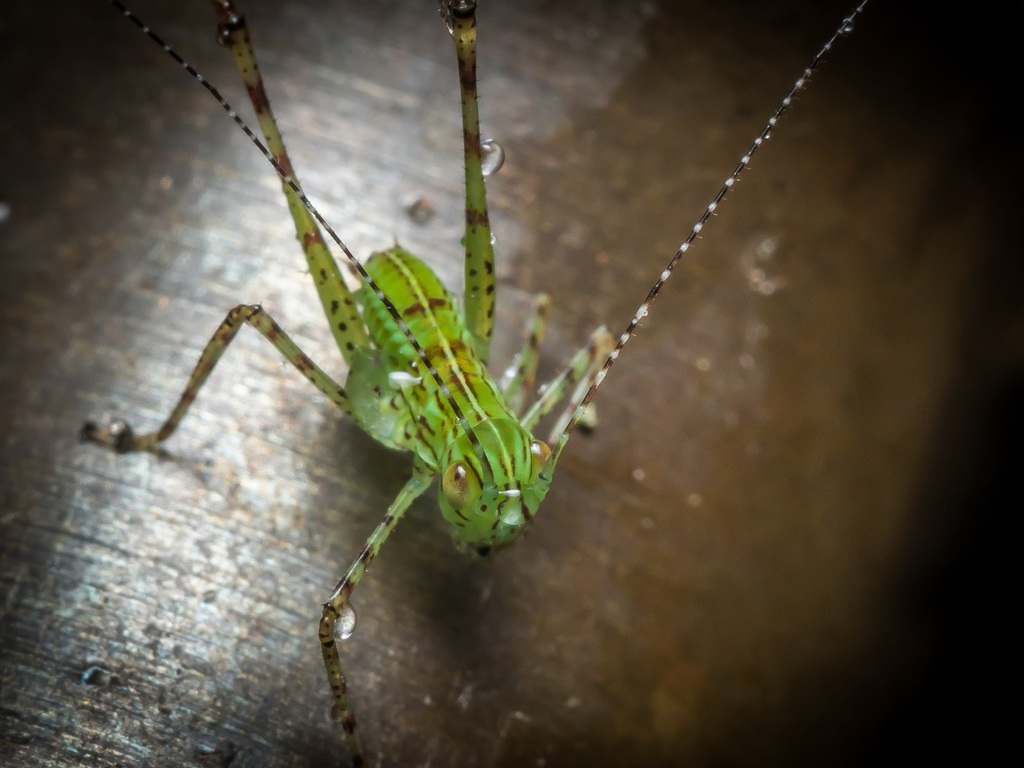


The Phaneropterinae, the sickle-bearing bush crickets or leaf katydids, are a subfamily of insects within the family Tettigoniidae. Nearly 2,060 species in 85 genera throughout the world are known. They are also known as false katydids or round-headed katydids.
The name Phaneropterinae is based upon the Old World genus Phaneroptera (type species P. falcata), meaning \visible wing\; this refers to the exposed tips of the inner wings seen in many species, although some genera, notably in the tribes Barbitistini and Odonturini have become brachypterous.
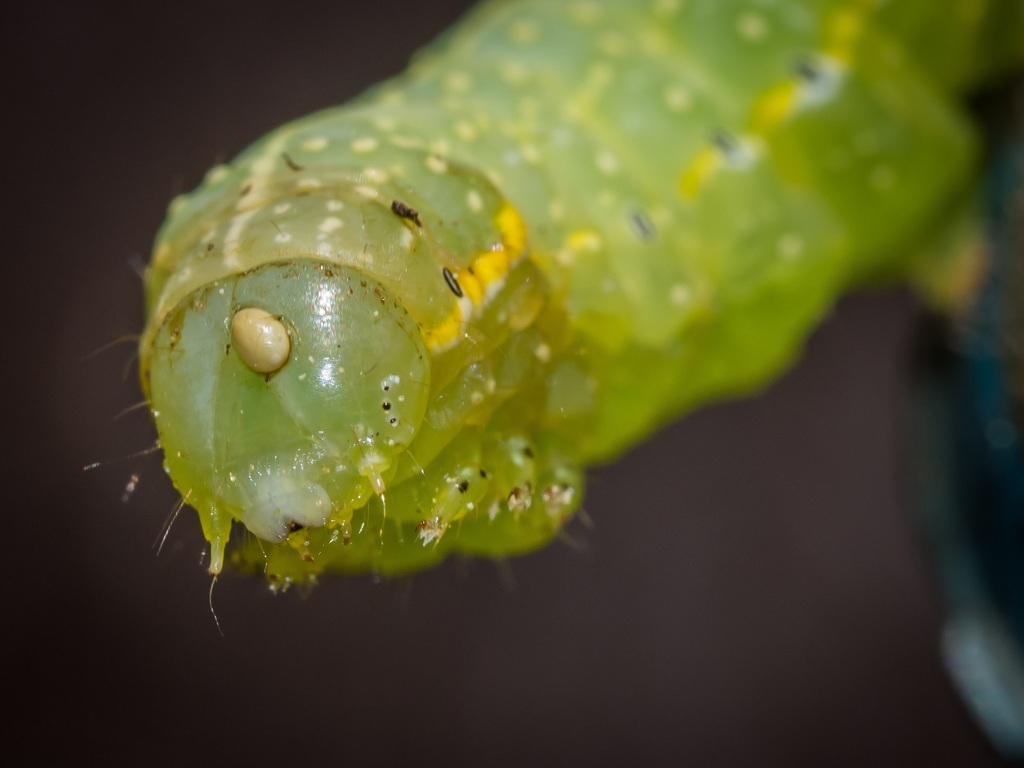



Amphipyrinae is a subfamily of owlet moths in the family Noctuidae. There are more than 50 genera and 210 described species in Amphipyrinae, although the classifications are likely to change over time.
This subfamily has been used as a catchall for members of Noctuidae that don't fit well into other subfamilies. As such, many of its members lack morphological traits that would allow assignment into one of the other subfamilies. Genetic analysis conducted on Amphipyrinae is improving the classification of these genera.
In 2021, phylogenetic research resulted in 11 genera being transferred from Amphipyrinae to six different subfamilies, and it is expected that more members of Amphipyrinae will be reassigned as further research is done.
Psaphidini is included here as a tribe, but is sometimes treated as the subfamily Psaphidinae. The Australian genera in Acronictinae are sometimes considered part of Amphipyrinae.

The Argentine ant (Linepithema humile, formerly Iridomyrmex humilis) is an ant native to northern Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia and southern Brazil. This invasive species was inadvertently introduced by humans on a global scale and has become established in many Mediterranean climate areas, including South Africa, New Zealand, Japan, Easter Island, Australia, Europe, Hawaii, and the continental United States. Argentine ants are significant pests within agricultural and urban settings, and are documented to cause substantial harm to communities of native arthropods, vertebrates, and plants within their invaded range.
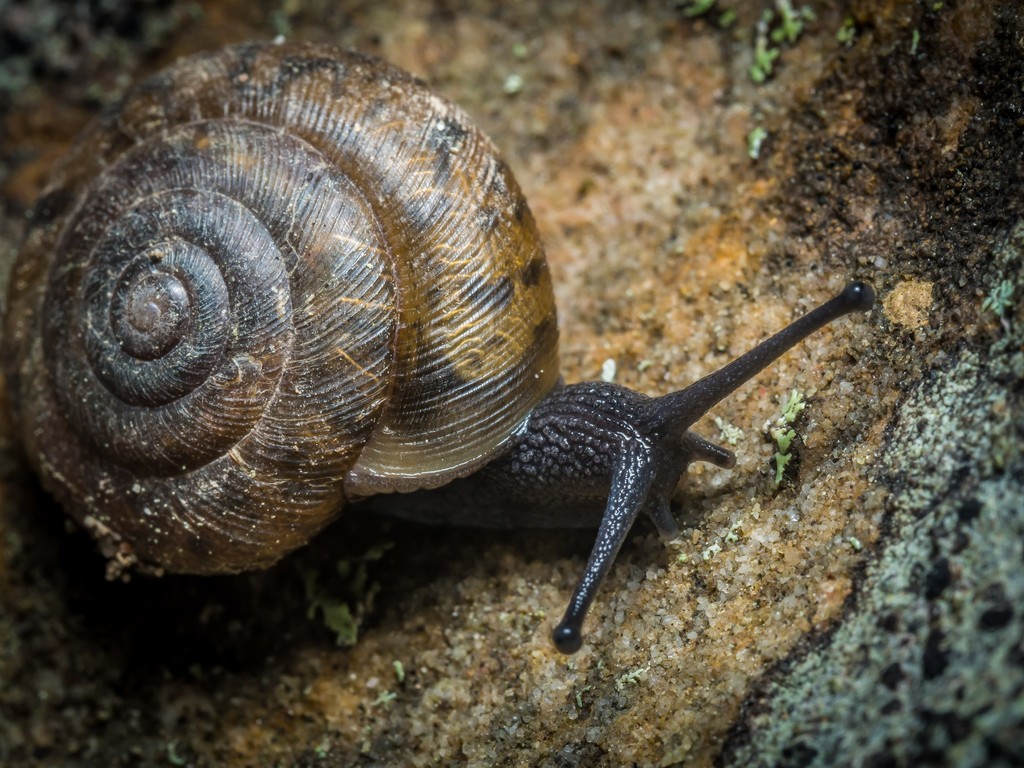

Helicoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the clade Stylommatophora.
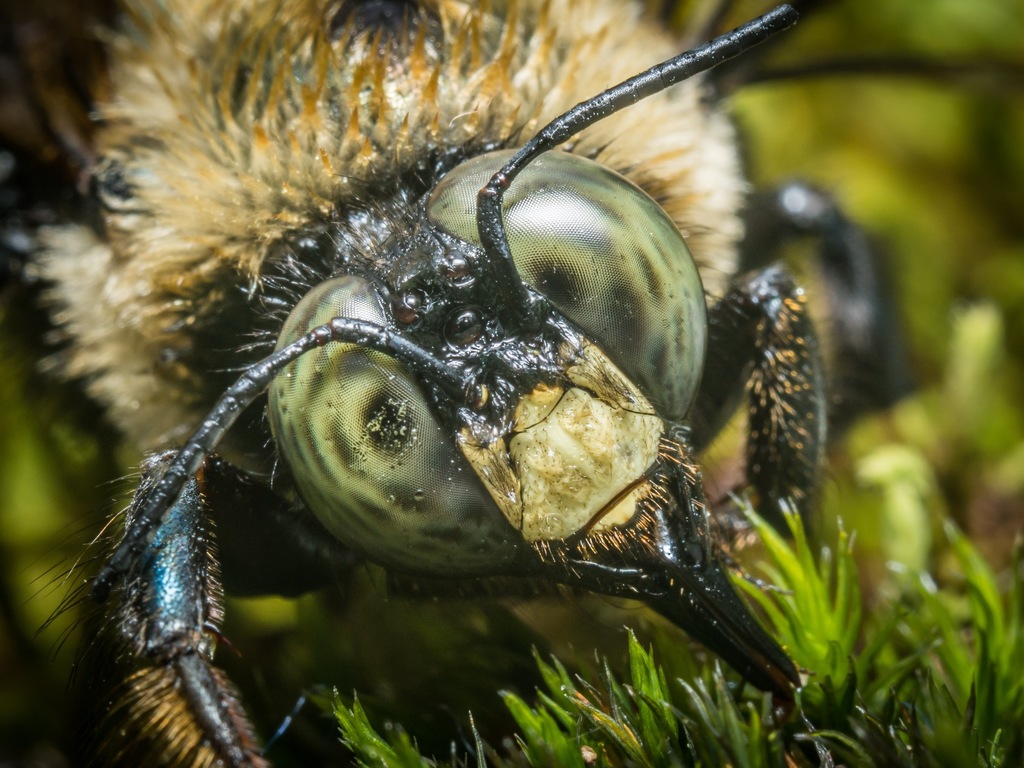
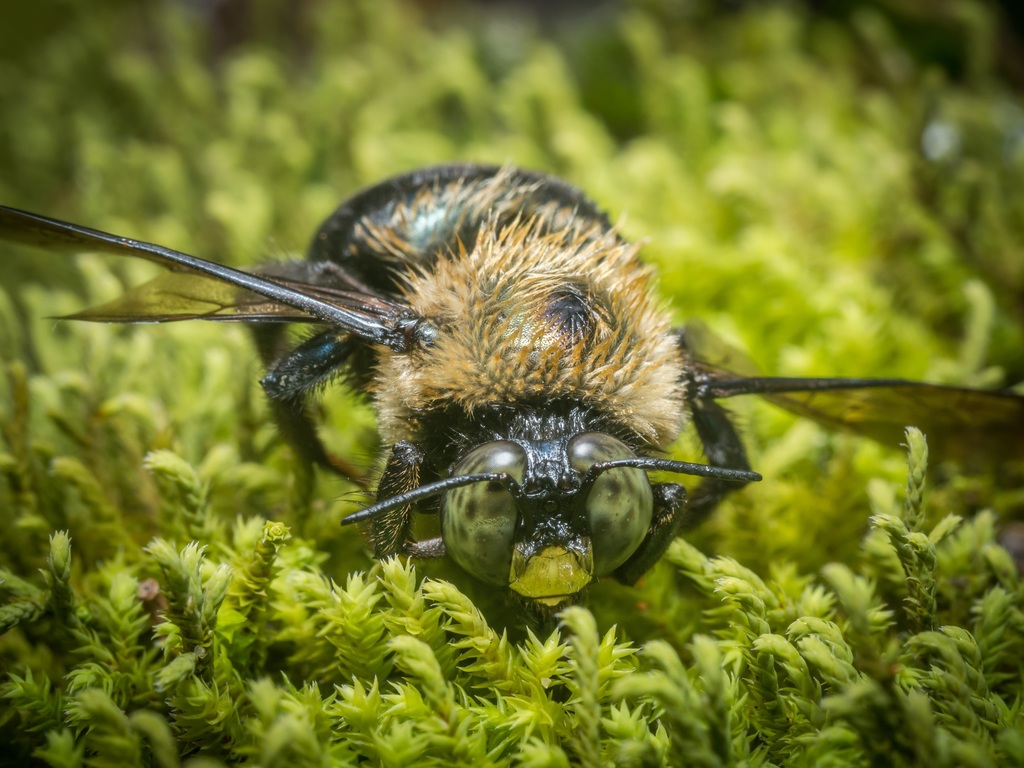


Xylocopa virginica, sometimes referred to as the eastern carpenter bee, extends through the eastern United States and into Canada. They are sympatric with Xylocopa micans in much of southeastern United States. They nest in various types of wood and eat pollen and nectar. In X. virginica, dominant females do not focus solely on egg-laying, as in other bee species considered to have \queens\. Instead, dominant X. virginica females are responsible for a full gamut of activities including reproduction, foraging, and nest construction, whereas subordinate bees may engage in little activity outside of guarding the nest.